Documentation Revision Date: 2019-09-05
Dataset Version: 1
Summary
This dataset contains 102 data files in netCDF (*.nc) format, with one file for each 16-day period from September 2014 to January 2019.
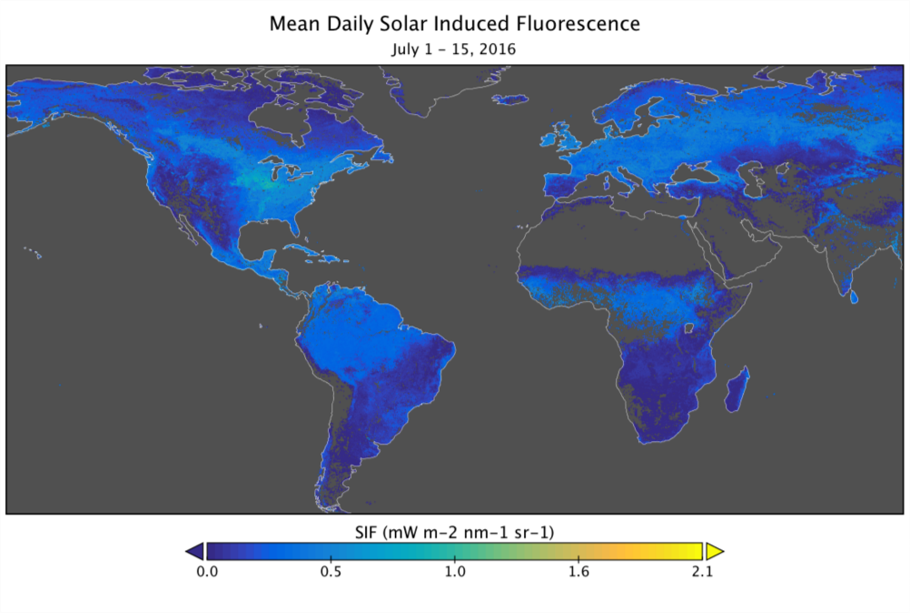
Figure 1: Predicted spatially contiguous SIF in the first half of July 2016. The highest SIF values during this time period were observed in agricultural sectors in the Northern Hemisphere.
Citation
Yu, L., J. Wen, C.Y. Chang, C. Frankenberg, and Y. Sun. 2019. High Resolution Global Contiguous SIF Estimates Derived from OCO-2 SIF and MODIS. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1696
Table of Contents
- Dataset Overview
- Data Characteristics
- Application and Derivation
- Quality Assessment
- Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
- Data Access
- References
Dataset Overview
This dataset provides high-resolution, spatially-contiguous, global solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) estimates at 0.05 degree (approx. 5 km at the equator) spatial and 16-day temporal resolution beginning in September 2014 and continuing to the present. This product, SIFoco2_005, was derived from Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) SIF observations was produced by training an artificial neural network (ANN) on the native OCO-2 SIF observations and MODIS BRDF-corrected seven-band surface reflectance along OCO-2's orbits. The trained ANN model was then applied to predict mean daily SIF (mW/m2/nm/sr) in OCO-2's gap regions based on MODIS reflectance and landcover. This framework was stratified by biomes and 16-day time steps. The high resolution and global contiguous coverage of this dataset will greatly enhance the synergy between satellite SIF and photosynthesis measured on the ground at consistent spatial scales. Potential applications of this dataset include advancing dynamic drought monitoring and mitigation, informing agricultural planning and yield estimation, and providing a benchmark for upcoming satellite missions with SIF capabilities at higher spatial resolutions.
Related Publication:
Yu, L., Wen, J., Chang, C. Y., Frankenberg, C., & Sun, Y. (2019). High-Resolution Global Contiguous SIF of OCO-2. Geophysical Research Letters, 46, 1449–1458. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL081109
Acknowledgements:
This work was supported by NASA's OCO-2 science team 80NSSC18K0895, Carbon Cycle Science NNX17AE14G, and Earth Science Division MEaSUREs programs.
Data Characteristics
Spatial Coverage: Global
Spatial Resolution: 0.05 degree grid (approx. 5 km at the equator)
Temporal Coverage: 2014-09-01 to 2019-01-31
Temporal Resolution: 15 to 16 days
Study Area: Global
Data File Information
This dataset contains 102 data files in netCDF v4 (*.nc) format, with one file for each 16-day period from September 2014 to January 2019.
User Note: Data files for dates 201504b, 201708a, 201708b, and 201709a are not available because there is no original OCO-2 SIF data due to instrument failure during these periods.
File Naming Convention: Example filename: sif_ann_201412b.nc
Files are named as sif_ann_YYYYMMx.nc, where YYYYMM represents the year and month, and x is either 'a' or 'b'. File names ending in 'a' represent the first half of each month and the files ending in 'b' represent the second half of the month. Note that 'ann' indicates that the data were modeled by an artificial neural network.
Spatial Reference System: Geographic latitude-longitude in decimal degrees
Data Variables:
Each file contains three variables: latitude, longitude, and 'sif_ann'. sif_ann represents the mean daily solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) in units of mW/m2/nm/sr for each 0.05 degree grid cell over 16-day time period.
The fill value for missing data is -999.
Application and Derivation
The high-resolution and global contiguous coverage of this data set will greatly enhance the synergy between satellite SIF and photosynthesis measured on the ground at consistent spatial scales. Potential applications with this data set include advancing dynamic drought monitoring and mitigation, informing agricultural planning and yield estimation in a more spatially explicit way, and providing a benchmark for upcoming satellite missions with SIF capabilities at higher spatial resolutions.
Quality Assessment
Validation of SIFoco2_005 was completed by 1) using a first validation approach to evaluate predictions, 2) comparisons with Chlorophyll Fluorescence Imaging Spectrometer (CFIS) airborne measurements, and 3) comparisons with global patterns in the original OCO-2 retrievals. For details, see Yu et al. (2019).
Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
The overall strategy of the prediction framework was to (1) use an artificial neural network (ANN) algorithm to train the native OCO-2 SIF from orbital swaths against MODIS BRDF-corrected reflectance data (MCD43A4 and MCD43C4 V006) and (2) apply the trained ANN models to predict SIF in OCO-2’s orbital gaps using spatially contiguous MODIS datasets as predictors. The authors derived distinct ANN models specific to each IGBP (International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme) biome type at each time step based on MODIS land cover products (MCD12Q1 for training and MCD12C1 for prediction).
See Yu et al. (2019) for details on input and validation data and the ANN prediction framework.
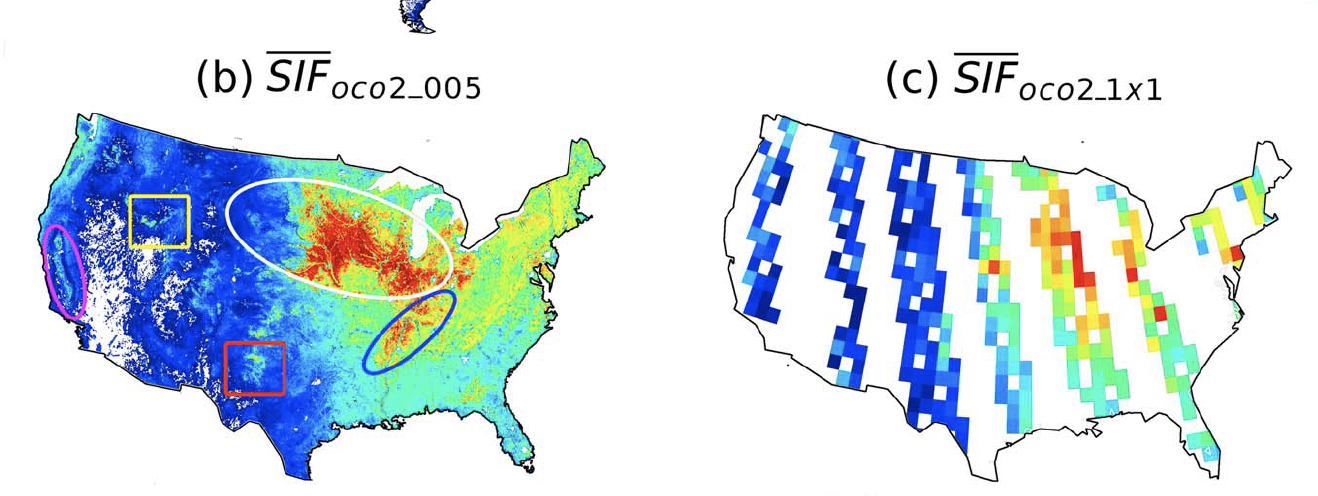
Figure 2. Predicted spatially contiguous SIFoco2_005 in the first 16 days of August 2015 for the United States (b) and SIFoco2 orbital swath data aggregated to a 1° grid (c). Ovals in (b) highlight the U.S. Midwestern corn belt (white), the rice belt along the lower Mississippi river (blue), and the California central valley (pink). Boxes highlight production areas for barley in Idaho (yellow) and cotton in northwestern Texas (red). (From Yu et al, 2019, Figure 2)
Data Center Processing: The ORNL DAAC obtained the SIFoco2_005 data files with the permission of the authors (Yu, et al., 2019) from https://cornell.app.box.com/s/cavtg50y80udbdirg022gm5whugmth02. The data center performed value-added processing to correct errors in the latitude and longitude variables, incorporate a fill value for missing data (-999), and to ensure that the files follow the Climate and Forecasting Conventions (CF 1.6).
Data Access
These data are available through the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC).
High Resolution Global Contiguous SIF Estimates Derived from OCO-2 SIF and MODIS
Contact for Data Center Access Information:
- E-mail: uso@daac.ornl.gov
- Telephone: +1 (865) 241-3952
References
Yu, L., Wen, J., Chang, C. Y., Frankenberg, C., & Sun, Y. (2019). High-Resolution Global Contiguous SIF of OCO-2. Geophysical Research Letters, 46, 1449–1458. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL081109