Documentation Revision Date: 2019-04-25
Dataset Version: 1
Summary
The mechanistic approach helps to improve the timing and spatial distribution of estimates of soil N emissions by accounting for actual biogeochemical processes that generate these emissions under varied soil conditions and vegetation types so that nitrification and denitrification can be represented. For non-agricultural biomes, the new mechanistic scheme uses a global soil nutrient dataset in an updated C and N mineralization framework. This enables the model to track the conversion of organic soil N to NH4 and NO3 pools on a daily scale for non-agricultural soils.
There are eight data files with this dataset. This includes one compressed file (.zip) with seven Fortran source codes (*.F), five input data files in NetCDF (.nc) format and two output files in NetCDF (.nc) format. A companion file is provided which contains instructions on how to build and run the new mechanistic soil nitrogen (N) module in-line with CMAQ version 5.1.
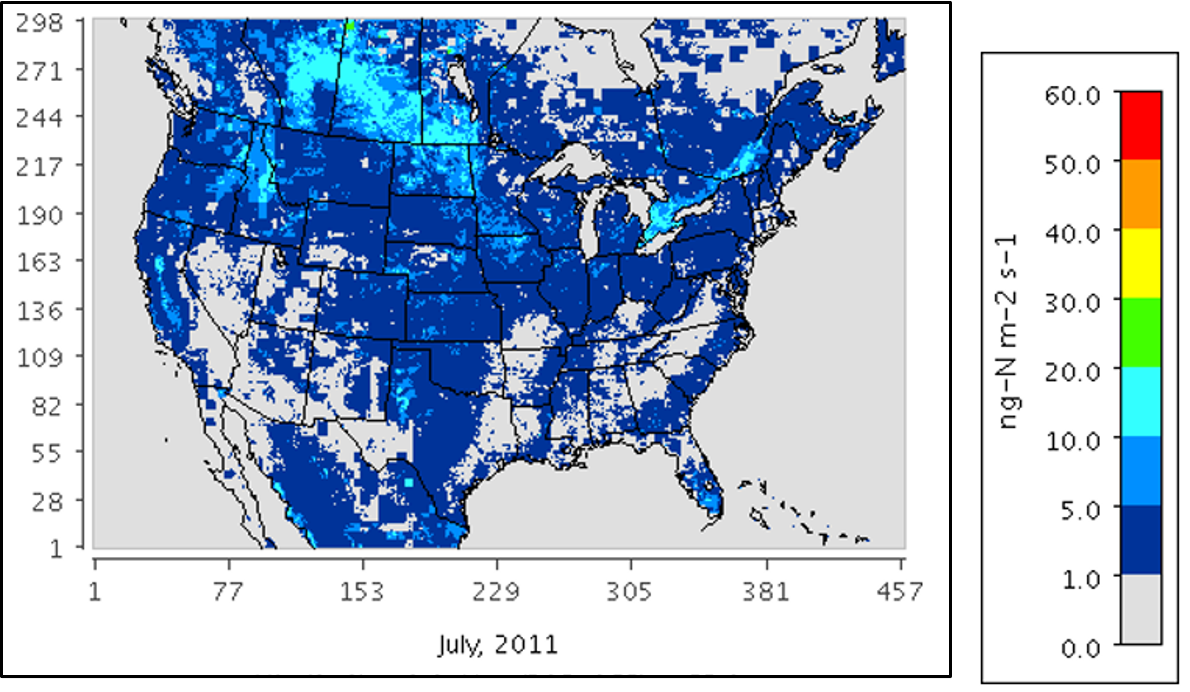
Figure 1. Soil N2O emissions on a monthly average basis for July 2011 estimated with mechanistic scheme. From Rasool et al. (2019).
Citation
Rasool, Q.Z., J.O. Bash, and D.S. Cohan. 2019. Mechanistic Module for Soil Nitrogen Emissions for CMAQ Model, North America, 2011. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1661
Table of Contents
- Dataset Overview
- Data Characteristics
- Application and Derivation
- Quality Assessment
- Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
- Data Access
- References
Dataset Overview
This model product provides source code, input data files, and example model outputs for a new mechanistic soil nitrogen (N) module in-line with the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model 5.1 to simulate nitric oxide (NO), nitrous acid (HONO), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ammonia (NH3) soil emissions. The modeling domain covers the continental USA plus portions of northern Mexico and southern Canada, extending from 25° N to 52° N. The simulations use a 12-km spatial grid resolution. Input data are from high-quality reference sources for year 2011. Example model output data are provided for one day, April 21, 2011.
The mechanistic approach helps to improve the timing and spatial distribution of estimates of soil N emissions by accounting for actual biogeochemical processes that generate these emissions under varied soil conditions and vegetation types so that nitrification and denitrification can be represented. For non-agricultural biomes, the new mechanistic scheme uses a global soil nutrient dataset in an updated C and N mineralization framework. This enables the model to track the conversion of organic soil N to NH4 and NO3 pools on a daily scale for non-agricultural soils.
Related Dataset:
Rasool, Q.Z., R. Zhang, D.S. Cohan, E.J. Cooter, L.N. Lamsal, J.O. Bash, and B. Lash. 2016. BDSNP Module for Improved Soil NO Emission Estimates for CMAQ Model, Conterminous USA. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1351
Related Publication:
Rasool, Q.Z., Bash, J.O. and Cohan, D.S., 2019. Mechanistic representation of soil nitrogen emissions in the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model v 5.1. Geoscientific Model Development, 12(2), pp.849-878. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-12-849-2019.
Acknowledgements:
This research was funded by a NASA ROSES (Research Opportunities in Earth and Space Science) grant, number NNX15AN63G.
Data Characteristics
Spatial Coverage: Continental US, portions of northern Mexico and southern Canada
Spatial Resolution: 12 x 12 km grid
Temporal Coverage: Input data are from high-quality reference sources for year 2011. Example model output data are provided for one day, April 21, 2011.
Temporal Resolution: Model run and data aggregation specific per user needs.
Study Area (coordinates in decimal degrees)
| Site | Westernmost Longitude | Easternmost Longitude | Northernmost Latitude | Southernmost Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continental US, portions of northern Mexico and southern Canada | -128.7422132 | -59.13283825 | 51.55248055 | 25.06967334 |
Data File Information
There are eight data files with this dataset. This includes one compressed file (.zip) with seven Fortran source codes (*.F), five input data files in NetCDF (.nc) format and two output files in NetCDF (.nc) format.
The companion file Mechanistic_Soil_N_Module_UserGuide.pdf provides instructions on how to build and run the new mechanistic soil nitrogen (N) module in-line with CMAQ version 5.1.
Table 1. Data file descriptions
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| Model source code files | |
|
cmaq-n-module-source.zip |
A compressed file which provides the seven source code files |
| Ncycling.F | Addresses soil N emissions |
| vdiffacmx.F | The original code for dry and wet deposition, vdiffacm2.F and cldproc_acm.F respectively modified to obtain total mass of N per area deposited to the ground from atmosphere |
| CNnonAgcycling.F | Addresses soil N emissions for non-agricultural biome |
| cldproc_acm.F | The original code for dry and wet deposition, vdiffacm2.F and cldproc_acm.F respectively modified to obtain total mass of N per area deposited to the ground from atmosphere |
| canopy_nox_mod.F | Canopy reduction factor for incorporating canopy reduction of soil NO as proposed by Hudman et al. (2012) |
| BIOG_EMIS.F | Biogenic emissions |
| BDSNP_MOD_EPIC.F | Used to call the new Ncycling.F and CNnonAgcycling.F to pass the computed soil NO, HONO and N2O into the biogenic emission outpus (B3GTS_S) |
|
Input files |
|
| SMNRESFILE.nc | Soil organic nitrogen data used to drive the C and N cycling based on Schimel and Weintraub (2003) for non-agricultural regions, where EPIC is not applicable |
| SMCRESFILE.nc | Soil organic carbon data used to drive the C and N cycling based on Schimel and Weintraub (2003) for non-agricultural regions, where EPIC is not applicable |
| PHTOPSOILFILE.nc | Soil pH, gridded for the CONUS domain |
| LANDFRACFILE.nc | Soil biome types. CMAQ by default uses 40-category NLCD Land Use classification (NLCD40) with sub-grid fractions for different land use |
| CNRATIOFILE.nc | Microbial C:N ratio |
|
Output files |
|
| N2O_EMIS_SOILINP_CMAQ51_FILE_20110421.nc | Soil N2O emission estimates and relevant diagnostics calculated for 20110421 |
| NOandHONO_B3GTS_S_CMAQv51_FILE_20110421.nc | Soil NO and HONO emissions estimates calculated for 20110421 along with other biogenic emissions that act as input to CMAQ's chemical transport model unlike the diagnostic N2O estimates |
NetCDF file properties
All *.nc files are in Lambert Conformal Conic Projection:
OGC WKT :
PROJCS["unnamed",
GEOGCS["unnamed ellipse",
DATUM["unknown",
SPHEROID["unnamed",6370000,0]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0],
UNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433]],
PROJECTION["Lambert_Conformal_Conic_2SP"],
PARAMETER["standard_parallel_1",33],
PARAMETER["standard_parallel_2",45],
PARAMETER["latitude_of_origin",40],
PARAMETER["central_meridian",-97],
PARAMETER["false_easting",0],
PARAMETER["false_northing",0],
UNIT["Meter",1]]
Resolution: 12- by 12-km grid
No data value: -2147483647
Table 2. Variables in the Input Files
| Filename | Variable | Units/format | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMNRESFILE.nc | SMN30cm | g N/m2 | Soil organic nitrogen data used to drive the C and N cycling |
| SMCRESFILE.nc | SMC30cm | g C/m2 | Soil organic carbon data used to drive the C and N cycling |
| PHTOPSOILFILE.nc | pHsl | n/a | Soil pH |
| LANDFRACFILE.nc | LANDFRAC | n/a | BIOME Classification based on NLCD40 |
| CNRATIOFILE.nc | CN30cm | percent | Carbon to nitrogen ratio |
Variables in the Output Files
Table 3. N2O_EMIS_SOILINP_CMAQ51_FILE_20110421.nc
* Denotes diagnostic parameters
| Variable | Units/format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DENITR_rate | kg/ha/s | Denitrification rate from Ncycling routine* |
| N2O_EMIS | g N/hr | N2O emission from Ncycling routine* |
| NH4_Pool | kg N/ha | NH4 Pool from Ncycling routine* |
| NITR_Rate | kg/ha/s | Nitrification rate from Ncycling routine* |
| NO3_Pool | kg N/ha | NO3 Pool from Ncycling routine* |
| PFACTOR | 0-1 | NO emission current pulse factor |
| DRYPERIOD | hr | Length of the dry period |
| NDEPRES | g N/m2 | Soil N reservoir from deposition |
| SOILMPREV | m3/m3 | Soil moisture ratio for previous time step |
| THETA_DIAG | 0-1 | Moisture water-filled pore space * |
| WET_TERM_DIAG | 0-1 | Moisture scale factor * |
| TEMP_DIAG | K | Temperature in last simulation hour * |
| TEMP_TERM_DIAG | Temperature scale factor* | |
| A_DIAG | 0-1 | Base emission factor from soil biome type * |
| NRES_FERT_DIAG | 0-1 | NRES fertilizer only * |
| AFERT_DIAG | 0-1 | Fertilizer emission factor * |
| NDEPRATE_DIAG | gm/s | Daily average N deposition rate * |
| CRFAVG | 0-1 | Daily average canopy reduction factor * |
| PULSEAVG | 0-1 | Daily average pulse factor * |
Table 4. NOandHONO_B3GTS_S_CMAQv51_FILE_20110421.nc
Units are grams per second for a 12- by 12-km grid cell.
| Variable | Units/format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ALDX | gm/s | Propionaldehyde and higher aldehydes |
| ALD2 | gm/s | Acetylaldehyde |
| BPIN | gm/s | b-PINENE |
| APIN | gm/s | a-PINENE |
| CO | gm/s | Carbon monoxide |
| ETH | gm/s | Ethene |
| ETHA | gm/s | Ethane |
| ETOH | gm/s | Ethanol |
| FORM | gm/s | Formaldehyde |
| HONO | gm/s | Nitrous acid |
| IOLE | gm/s | Internal olefin carbon bond (R-C=C-R) |
| ISOP | gm/s | Isoprene |
| MEOH | gm/s | Methanol |
| NO | gm/s | Nitric oxide |
| OLE | gm/s | Terminal olefin carbon bond (R-C=C) |
| PAR | gm/s | Paraffin carbon bond (C-C) |
| SESQ | gm/s | Sesquiterpene |
| TERP | gm/s | Terpene |
Application and Derivation
The mechanistic module helps to improve the timing and spatial distribution of estimates of soil N oxide emissions by accounting for actual mechanistic process that generate these emissions under varied soil conditions, nutrient availability and meteorology regional model.
Quality Assessment
The corresponding modeled estimates from the new mechanistic soil N module have been compared to OMI tropospheric NO2 columns, SEARCH campaign NOx concentrations and secondary pollutant concentrations like Ozone and PM2.5 NO3 observed from IMPROVE, AQS, CSN and CASTNET observation networks. Statistical performance of modeled vs observed values was thoroughly analyzed for May and July 2011 for Conterminous US and both improvement and uncertainty in model performance is explained in Rasool et al. (2019).
Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
The new mechanistic module has been implemented into the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) modeling system v5.1 to produce soil NO, HONO, and N2O emission estimates using the soil temperature/moisture information from the Pleim-Xiu land surface model (Pleim and Xiu, 2003) in the Weather Research Forecasting (WRF) model v 3.7. The Mechanistic module helps to improve the timing and spatial distribution of estimates of soil N oxide emissions by accounting for actual mechanistic process that generate these emissions under varied soil conditions, nutrient availability and meteorology.
Based on the mechanistic scheme, soil NO, HONO, and N2O emissions at each modeling grid and time-step are determined by accounting for soil nitrogen (either form the fertilizer application during the growing season or the soil N naturally available in non-agricultural biome or the nitrogen dry/wet deposition from the atmosphere), and the subsequent transformation of soil nitrogen either through nitrification or denitrification depending on variables such as, soil temperature and moisture, availability of soil NH4 or NO3, relative availability of NO3 to C, soil pH, gas diffusivity, the soil pulsing after precipitation, and the canopy reduction due to the resistance (Rasool et al., 2019).
New codes in the mechanistic module
The mechanistic module is simultaneously compiled with other executables of the CMAQ Chemistry-Transport Model (CCTM). CCTM integrates model-ready inputs such as emissions, meteorology, photochemistry, initial and boundary conditions to simulate continuous atmospheric chemical conditions at user-defined time frequency (hourly, daily etc.). Implementation of the mechanistic module in-line with CCTM ensures that soil NO, HONO and N2O as per newly proposed mechanistic scheme is also accounted for while generating gridded and temporally resolved air pollutant concentrations as output.
Ncycling.F and CNnonAgcycling.F:
Ncycling.F and CNnonAgcycling.F were added as global attributes in the CCTM source code repository, which basically gives the mechanistic representation of soil NO, HONO, and N2O emissions which are passed into the biogenic emission outputs (Rasool et al., 2019).
Environmental variables specific to mechanistic module
Understanding the environment variables defined in the mechanistic module is crucial for the real case implementation and further model development if needed.
LANDFRACFILE.F:
CMAQ v5.1 has sub-grid scale representation for 40 National Land Cover dataset (NLCD) biomes and was thus utilized rather than the MODIS 24 classification.
SMCRESFILE, SMNRESFILE, CNRATIOFILE, and PHTOPSOILFILE:
The input files SMCRESFILE, SMNRESFILE, CNRATIOFILE and PHTOPSOILFILE provide the soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools, microbial C:N ratio and soil pH respectively over the simulation domain. These inputs are used in the mechanistic module to drive the C and N cycling based on Schimel and Weintraub (2003) for non-agricultural regions. For the modeling grid, non-agricultural grids can be classified from ‘LANDFRFILE’ and MODIS to NLCD mapping algorithm coded in mechanistic scheme source codes (Rasool et al., 2019).
Refer to the companion file Mechanistic_Soil_N_Module_UserGuide.pdf for detailed instructions for building and executing the module in-line with CMAQ version 5.1.
Data Access
These data are available through the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC).
Mechanistic Module for Soil Nitrogen Emissions for CMAQ Model, North America, 2011
Contact for Data Center Access Information:
- E-mail: uso@daac.ornl.gov
- Telephone: +1 (865) 241-3952
References
Hudman, R.C., A.R. Russell, L.C. Valin, and R.C. Cohen.: Interannual variability in soil nitric oxide emissions over the United States as viewed from space, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 10, 9943-9952. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-9943-2010
Pleim, J.E. and A. Xiu: Development of a land surface model. Part II: Data assimilation. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 42(12), pp.1811-1822, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(2003)042<1811:DOALSM>2.0.CO;2
Rasool, Q.Z., Bash, J.O. and Cohan, D.S., 2019. Mechanistic representation of soil nitrogen emissions in the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model v 5.1. Geoscientific Model Development, 12(2), pp.849-878. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-12-849-2019.
Rasool, Q.Z., R. Zhang, B. Lash, D.S. Cohan, E.J. Cooter, J.O. Bash, and L.N. Lamsal. 2016. Enhanced representation of soil NO emissions in the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model version 5.0.2. Geosci. Model Dev., 9: 3177-3197. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-9-3177-2016
Schimel, J.P. and M.N. Weintraub: The implications of exoenzyme activity on microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in soil: a theoretical model, Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 35, 549-563, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00015-4