Documentation Revision Date: 2025-02-20
Dataset Version: 1
Summary
The MASTER instrument is a modified Daedalus Wildfire scanning spectrometer that flies on a variety of multi-altitude research aircraft and provides spectral information similar to that provided by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER), which are aboard two NASA Earth Observing System satellites: Terra and Aqua. The primary goal of this airborne campaign was to demonstrate important science and applications research that is uniquely enabled by the full suite of MASTER thermal infrared bands as well as the contiguous spectroscopic measurements of the AVIRIS (also flown in similar campaigns), or combinations of measurements from both instruments.
This dataset includes a total of 336 data files: 39 files in Hierarchical Data Format (HDF-4; *.hdf) format, 156 ENVI raster files (*.dat and *.hdr) that are compressed (*.zip), 39 files in Keyhole Markup Language Zipped (KMZ; *.kmz) format, 39 Portable Network Graphics (PNG; *.png) files that are compressed (*.zip), 16 text (*.txt) files, 4 archives of text files that are zipped (*.zip), 4 flight maps as GIF (*.gif) images, and 39 browse images in JPEG (*.jpg) format.
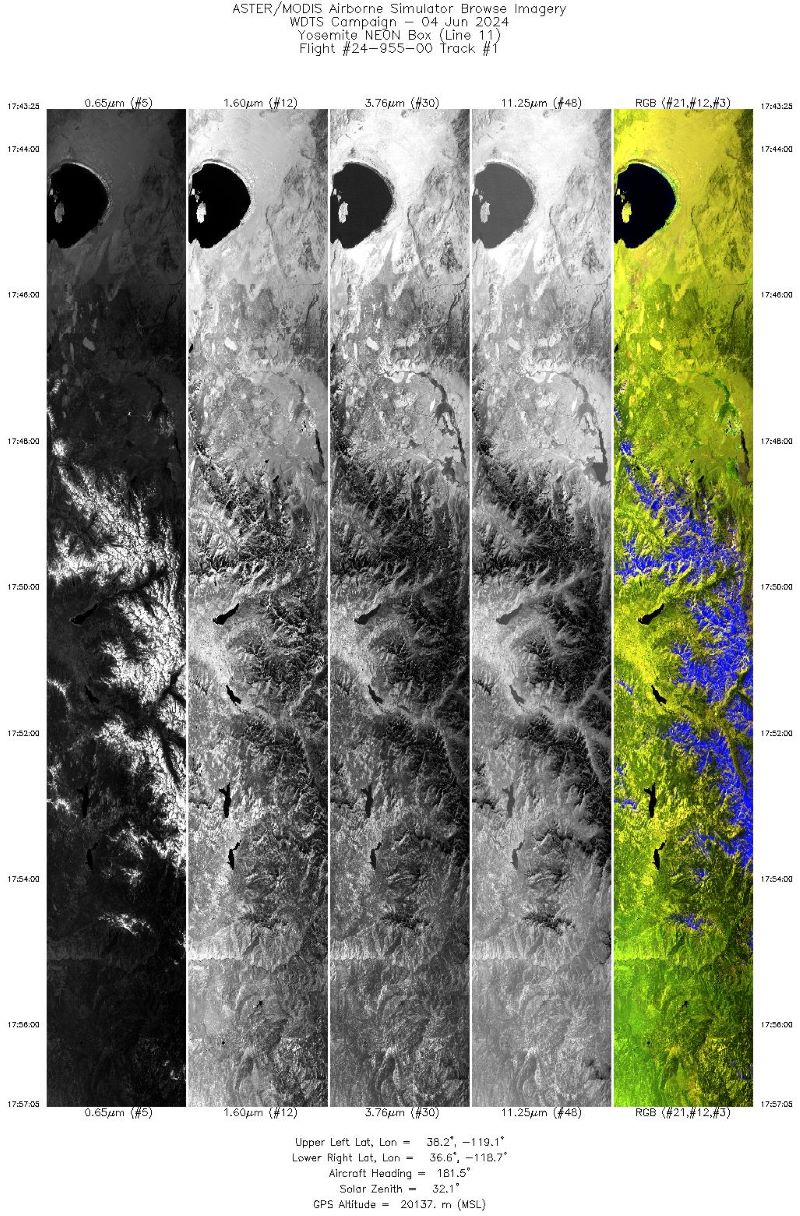
Figure 1. Single band images and an RGB composite image from flight track 1 acquired on 04 June 2024 over Sierra National Forest in eastern California, US, centered south of Mono Lake (approx. 37.20 lat, -118.80 lon). Source: MASTERL1B_2495500_01_20240604_1743_1757_V01.jpg
Citation
Hook, S.J., J.S. Myers, K.J. Thome, M. Fitzgerald, A.B. Kahle, Airborne Sensor Facility NASA Ames Research Center, and R.O. Green. 2025. MASTER: Western Diversity Time Series Campaign, WDTS, Spring 2024. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2383
Table of Contents
- Dataset Overview
- Data Characteristics
- Application and Derivation
- Quality Assessment
- Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
- Data Access
- References
- Dataset Revisions
Dataset Overview
This dataset includes Level 1B (L1B) data products from the MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator (MASTER) instrument. The spectral data were collected as part of the Western Diversity Time Series (WDTS, formerly HyspIRI) airborne campaign during four flights aboard a NASA ER-2 aircraft over California and Nevada, U.S., from 2024-06-04 to 2024-06-28. The WDTS campaign will observe California's ecosystems and provide critical information on natural disasters such as volcanoes, wildfires, and drought. MASTER products can identify vegetation type and health and provide a benchmark for the state of the ecosystems against which future changes can be assessed. Data products include L1B georeferenced multispectral imagery of calibrated radiance in 50 bands covering wavelengths of 0.460 to 12.879 micrometers at approximately 50-meter spatial resolution. Derived L2 data products are emissivity in five bands in thermal infrared range (8.58 to 12.13 micrometers) and land surface temperature. The L1B file format is HDF-4, and L2 products are provided in ENVI and KMZ formats. In addition, the dataset includes the flight path, spectral band information, instrument configuration, ancillary notes, and summary information for each flight, and browse images derived from each L1B data file.
The Western Diversity Time Series (WDTS) is a NASA field investigation focusing on observing California’s ecosystems and providing critical information on natural disasters such as volcanoes, wildfires, and drought through multispectral imagery. WDTS collects seasonal visible to short wave infrared (VSWIR) and thermal infrared (TIR) airborne imagery using instruments including the Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS), MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator (MASTER), Hyperspectral Thermal Emission Spectrometer (HyTES), and Pushbroom Imager for Cloud and Aerosol Research and Development (PICARD) on a NASA ER-2 high-altitude platform. WDTS aims to provide a benchmark on the state of ecosystems against which future changes can be assessed. WDTS started in 2020 and is a continuation of the HyspIRI Airborne campaign in 2013-2018.
The MASTER instrument is a modified Daedalus Wildfire scanning spectrometer that flies on a variety of multi-altitude research aircraft and provides spectral information similar to that provided by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER), which are aboard two NASA Earth Observing System satellites: Terra and Aqua. MASTER provides data in 50 channels spanning visible to thermal infrared wavelengths (0.4 – 13 µm). Its data have been used to study geological patterns, land covers, ecological disturbances, and other phenomena that affect Earth surface properties.
Project: MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator
The MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator (MASTER) is a scanning spectrometer which flies on a variety of multi-altitude research aircraft and provides data similar to the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER). MASTER first flew in 1998 and has ongoing deployments as a Facility Instrument in the NASA Airborne Science Program (ASP). MASTER is a joint project involving the Airborne Sensor Facility (ASF) at the Ames Research Center, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), and the Earth Resources Observation and Science Center (EROS).
Related Publication
Hook, S.J. Myers, J.J., Thome, K.J., Fitzgerald, M. and A.B. Kahle. 2001. The MODIS/ASTER airborne simulator (MASTER) - a new instrument for earth science studies. Remote Sensing of Environment 76:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(00)00195-4
Related Datasets
Additional MASTER datasets are available on the ORNL DAAC MASTER project page.
Acknowledgments
The MASTER instrument is maintained and operated by the Airborne Sensor Facility (ASF) at NASA Ames Research Center in Mountain View, California, under the oversight of the EOS Project Science Office at NASA Goddard. Data processing was conducted at NASA Ames Research Center and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, California.
Data Characteristics
Spatial Coverage: Portions of California and western Nevada, U.S.
Spatial Resolution: 50 m
Temporal Coverage: 2024-06-04 to 2024-06-28
Temporal Resolution: One-time estimate
Study Area: Latitude and longitude are given in decimal degrees.
| Site | Northernmost Latitude | Southernmost Latitude | Easternmost Longitude | Westernmost Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| California; western Nevada | 40.980 | 31.952 | -112.500 | -123.750 |
Data File Information
This dataset includes a total of 336 data files: 39 files in Hierarchical Data Format (HDF-4; *.hdf) format, 156 ENVI raster files (*.dat and *.hdr) that are compressed (*.zip), 39 files in Keyhole Markup Language Zipped (KMZ; *.kmz) format, 39 Portable Network Graphics (PNG; *.png) files that are compressed (*.zip), 16 text (*.txt) files, 4 archives of text files that are zipped (*.zip), 4 flight maps as GIF (*.gif) images, and 39 browse images in JPEG (*.jpg) format.
There are different numbers of each type of file, which corresponds to the number of "flights" and "flight tracks". A "flight" is flown on a single day, and a "flight track" typically refers to a segment of a given flight. The number of flight tracks varies among flights (Table 2).
- There are four flights with 39 flight tracks (Table 2).
- For each flight track, there is at least one L1B data file in HDF format and an auxiliary browse image (*.jpg).
- L2 data are included for each flight track. For each track, there are five L2 data files in ZIP format.
- Four of the ZIP files contain L2 ENVI data for emissivity, land surface temperature, geographic coordinates, and quality assurance status. Each ZIP includes a binary data file (*.dat) and its header file (*.hdr).
- One ZIP file contains three L2 PNG files: RBG composite, single-band emissivity, and land surface temperature.
- L2 land surface temperture (*LST.kmz) in KMZ format.
- For each flight, there is a collection of auxiliary files providing information about the flight and instrument configuration.
The primary data files are named MASTERL1B_BBBBBBB_CC_YYYYMMDD_EEFF_GGHH_V0J-X.ext (e.g., MASTERL1B_2364200_10_20230405_1949_1955_V01.hdf).
The flight track-level browse images are named MASTERL1B_BBBBBBB_CC_YYYYMMDD_EEFF_GGHH_V0J.jpg (e.g., MASTERL1B_2364200_10_20230405_1949_1955_V01.jpg).
The deployment-level auxiliary files are named MASTER_BBBBBBB_YYYYMMDD_X.ext (e.g., MASTER_2364200_20230405_config.txt).
Elements of file names are described as:
BBBBBBB = the flight number (see Table 2),
CC = flight track,
YYYYMMDD = date of sampling,
EEFF = starting time at EE hour and FF minute,
GGHH = ending time at GG hour and HH minute,
J = version number for file ("1", "2", or "3"),
X = the file content (see Table 1), and ext = "hdf", "kmz", "gif", "jpg", "txt", or "zip", indicating the file extension.
Table 1. File names and descriptions.
| File Name | Level | File Type | Total Files | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Data Files | ||||
| MASTERL1B_BBBBBBB_CC_YYYYmmDD_EEFF_GGHH_V0J.hdf | L1B | HDF-4 | 39 | Multispectral radiance in 50 bands, pixel coordinates, sensor configuration, aircraft platform data, analysis parameters. The "CalibratedData" variable provides estimates of radiance in units of W m-2 sr-1 per micron. |
| MASTERL2_BBBBBBB_CC_YYYYmmDD_EEFF_GGHH_V0J-emissivity_tes.zip | L2 | ENVI | 39 | Map of atmospheric corrected emissivity; Temperature and Emissivity Separation (TES) corrected data in 5 bands (wavelengths: 8.58, 9.02, 10.62, 11.32, and 12.13 µm). |
| MASTERL2_BBBBBBB_CC_YYYYmmDD_EEFF_GGHH_V0J-images.zip | L2 | PNG | 39 | Three non-georeferenced images depicting (a) RGB composite using selected bands, (b) emissivity from a single band, and (c) land surface temperature. |
| MASTERL2_BBBBBBBB_CC_ YYYYmmDD_EEFF_GGHH_V0J-location.zip | L2 | ENVI | 39 | Latitude and longitude coordinates for pixels in ENVI files. |
| MASTERL2_BBBBBBB_CC_YYYYmmDD_EEFF_GGHH_V0J-LST.kmz | L2 | KMZ | 39 | Map of land surface temperature in degrees Kelvin. |
| MASTERL2_BBBBBBB_CC_YYYYmmDD_EEFF_GGHH_V0J-QAmap.zip | L2 | ENVI | 39 | QA status for each pixel from TES algorithm, where 1 = divergence and 0 = convergence. |
| MASTERL2_BBBBBBB_CC_YYYYmmDD_EEFF_GGHH_V0J-surface_temp.zip | L2 | ENVI | 39 | Map of land surface temperature (TES LST) in degrees Kelvin. |
| Auxiliary Files | ||||
| MASTERL1B_BBBBBBB_CC_YYYYMMDD_EEFF_GGHH_V0J.jpg | L1B | JPEG | 39 | Browse figures; one image per flight track; multiple tracks per flight. |
| MASTER_BBBBBBB_YYYYMMDD_ancillary.txt | - | Text | 4 | Ancillary information about flight including notes on aircraft platform, mission objective, and data evaluation. |
| MASTER_BBBBBBB_YYYYMMDD_config.txt | - | Text | 4 | Instrument configuration information for flight. |
| MASTER_BBBBBBB_YYYYMMDD_flightpath.gif | - | GIF | 4 | Map showing flight paths. |
| MASTER_BBBBBBB_YYYYMMDD_spectral_band_info.txt | - | Text | 4 | Spectral band information for flight. |
| MASTER_BBBBBBB_YYYYMMDD_spectral_response_table.zip | - | Text | 4 | Spectral response tables by band (ZIP archive of 50 text files). |
| MASTER_BBBBBBB_YYYYMMDD_summary.txt | - | Text | 4 | Time and coordinates for start and end of flight tracks along with the number of scan lines, solar and instrument angles, and aircraft altitude. FTLT = flight track number. |
Data File Details
The HDF-4 files contain swath trajectory data using longitude and latitude coordinates. The spatial resolution is approximately 50 m and is a function of aircraft altitude.
Table 2. Number of flight tracks for each MASTER flight during this 2024 deployment over California (CA) and Nevada (NV).
| Date | Flight Number | Locations (USA) | Flight Tracks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Level | L1B | L2 | ||
| 2024-06-04 | 2495500 | Yosemite NEON Box (Line 11) | 11 | 11 |
| 2024-06-21 | 2496000 | Lake Tahoe Box (Line 11) | 12 | 12 |
| 2024-06-26 | 2496200 | Santa Barbara Box (Line 1) | 7 | 7 |
| 2024-06-28 | 2496300 | Santa Barbara Box (Line 7) | 9 | 9 |
| Total | 39 | 39 | ||
Application and Derivation
The primary objective of MASTER is to: (a) collect ASTER-like and MODIS-like land datasets to support the validation of the ASTER and MODIS geophysical retrieval algorithms; (b) collect these datasets at a higher resolution than the spaceborne datasets to permit scaling studies and comparisons with in-situ measurements; and (c) under fly the EOS-AM1 ASTER and MODIS sensors to provide an additional radiometric calibration to assist with in-flight instrument performance characterization. Calibration is particularly important for ASTER where on-board calibration is dependent on a single black body in the TIR and only partial aperture illumination in the VNIR.
A secondary objective of MASTER is to: (a) provide both a backup instrument and backup modules for the current MODIS Airborne simulator, which is committed to a program of atmospheric and oceanic measurements; and (b) provide a wider spectral and dynamic range alternative to the use of the Thematic Mapper (TM) airborne simulator and Thermal Infrared Multispectral Scanner (TIMS) airborne scanners (JPL, 2021b).
MASTER imagery has been used for mapping wildfires and their impacts (Veraverbeke et al., 2011), land cover (Li and Moon, 2004), coral reefs (Capolsini et al., 2003), and urban heat islands (Zhao and Wentz, 2016).
Quality Assessment
The MASTER instrument channels are calibrated spectrally and radiometrically in the laboratory preflight and postflight. The mid-infrared and thermal infrared channels (26–50) are also radiometrically calibrated in-flight by viewing an internal hot and cold blackbody with each scanline (Hook et al., 2001). Three calibration and validation experiments were conducted in 1998–2001 (Hook et al., 2001; JPL, 2021a). Spectral response information for this deployment is included in the files named MASTER_BBBBBBB_YYYYMMDD_spectral_response_table.zip.
Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
The MASTER instrument was developed by the NASA Ames Research Center in conjunction with the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The instrument consists of three key components: the scanning spectrometer, the digitizer, and the storage system. The scanning unit was built by Sensys Technology (formerly Daedalus Enterprises) and the digitizer was a collaborative effort between Berkeley Camera Engineering and the Ames Airborne Sensor Facility (ASF, 2021). The data storage system and overall system integration were also provided by the ASF.
The MASTER instrument is similar to the MODIS Airborne Simulator (MAS) developed by the MODIS project (King et al., 1996). However, it has two key differences. First, MASTER supports a variety of scan speeds allowing it to acquire contiguous imagery from a variety of altitudes with different pixel sizes. Second, the channel positions are configured to closely match those of ASTER and MODIS. A detailed description of the instrument and optical system are provided by Hook et al. (2001) and King et al. (1996), respectively.
The Western Diversity Time Series (WDTS, formerly HyspIRI) program will observe California’s ecosystems and provide critical information on natural disasters such as volcanoes, wildfires, and drought. It will provide a benchmark on the state of the ecosystems against which future changes can be assessed, as the instruments will be capable of identifying vegetation type and health. The WDTS Airborne Campaign is a multi-year effort to collect seasonal VIS-SWIR and TIR airborne scanner data using both AVIRIS and MASTER remote sensing instruments aboard the ER-2 high-altitude platform (ASF, 2021).
For this campaign, the MASTER instrument was flown on NASA's ER-2 aircraft at altitudes of 19,500–20,360 m above sea level.
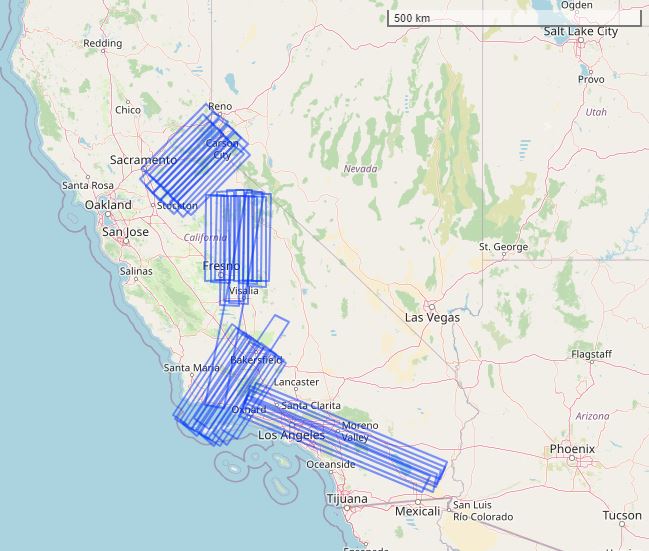
Figure 2. Flight tracks over California and Nevada represented as rectangular polygons. Basemap: © OpenStreetMap contributors.
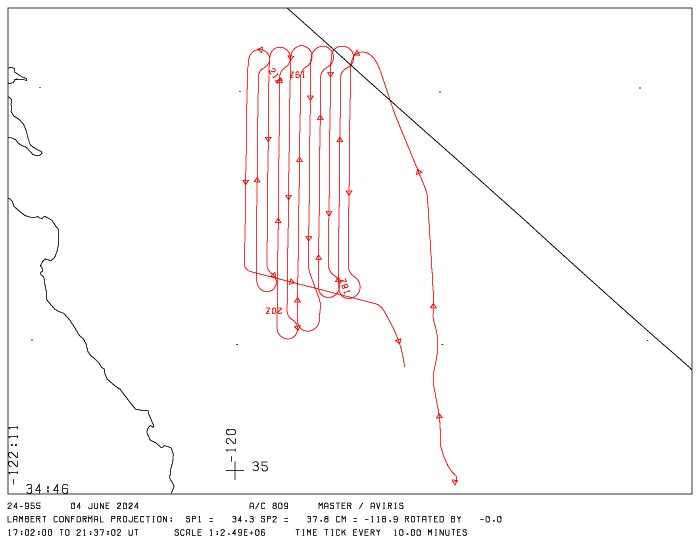
Figure 3. Typical flight path is shown for 04 June 2024. Flight 2495500 and 11 flight tracks occurred over California and Nevada. Source: MASTER_2495500_20240604_flightpath.gif
Data Access
These data are available through the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC).
MASTER: Western Diversity Time Series Campaign, WDTS, Spring 2024
Contact for Data Center Access Information:
- E-mail: uso@daac.ornl.gov
- Telephone: +1 (865) 241-3952
References
ASF. 2021. Campaign summary information: HyspIRI / WDTS Airborne Campaign. Airborne Sensor Facility, Airborne Science Program, NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California. https://asapdata.arc.nasa.gov/sensors/master/data/deploy_html/hyspiri_home.html
Capolsini, P., S. Andréfouët, C. Rion, and C. Payri. 2003. A comparison of Landsat ETM+, SPOT HRV, Ikonos, ASTER, and airborne MASTER data for coral reef habitat mapping in South Pacific islands. Canadian J. Remote Sensing 29:187-200. https://doi.org/10.5589/m02-088
Hook, S.J. Myers, J.J., Thome, K.J., Fitzgerald, M., and A.B. Kahle. 2001. The MODIS/ASTER airborne simulator (MASTER) - a new instrument for earth science studies. Remote Sensing of Environment 76:93-102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(00)00195-4
JPL. 2021a. Calibration and Validation, MASTER: MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator. Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, USA. https://masterprojects.jpl.nasa.gov/cal-val
JPL. 2021b. Science objectives, MASTER: MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator. Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, USA. https://masterprojects.jpl.nasa.gov/objectives
King, M.D., W.P. Menzel, P.S. Grant, J.S. Myers, G.T. Arnold, S.E. Platnick, L.E. Gumley, S.C. Tsay, C.C. Moeller, M. Fitzgerald, K.S. Brown, and F.G. Osterwisch. 1996. Airborne scanning spectrometer for remote sensing of cloud, aerosol, water vapor and surface properties. J. Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology 13:777-794. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0426(1996)013<0777:ASSFRS>2.0.CO;2
Li, P., and W.M. Moon. 2004. Land cover classification using MODIS-ASTER airborne simulator (MASTER) data and NDVI: A case study of the Kochang area, Korea. Canadian J. Remote Sensing 30:123-126. https://doi.org/10.5589/m03-061
Veraverbeke, S., S. Harris, and S. Hook. 2011. Evaluating spectral indices for burned area discrimination using MODIS/ASTER (MASTER) airborne simulator data. Remote Sensing of Environment 115:2702-2709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.06.010
Zhao, Q., and E.A. Wentz. 2016. A MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator (MASTER) imagery for urban heat island research. Data 1:7. https://doi.org/10.3390/data1010007
Dataset Revisions
| Version | Release Date | Revision Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 (update) | 2025-02-20 | L2 data products were appended to dataset. |
| 1.0 | 2024-12-04 | Initial publication |