Documentation Revision Date: 2026-02-05
Dataset Version: 1
Summary
There are two data files in cloud optimized GeoTIFF (.tif) format with this dataset.
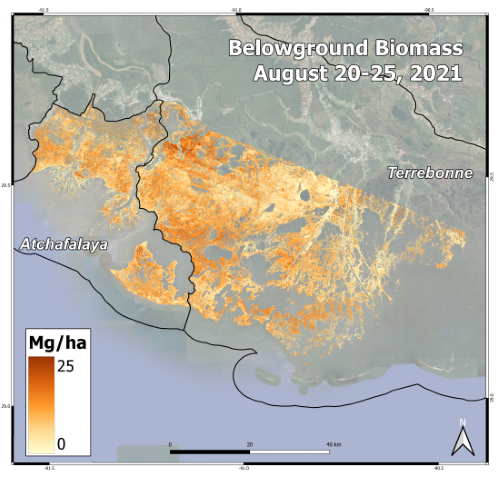
Figure 1. Herbaceous belowground biomass (Mg/ha) in the Atchafalaya and Terrebonne Basins, derived from AVIRIS-NG data collected during the Delta-X August 2021 campaign.
Citation
Jensen, D.J., E. Castañeda-Moya, E. Solohin, and M. Simard. 2026. Delta-X: AVIRIS-NG L3 Derived Herbaceous Belowground Biomass, MRD, LA, USA. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2456
Table of Contents
- Dataset Overview
- Data Characteristics
- Application and Derivation
- Quality Assessment
- Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
- Data Access
- References
Dataset Overview
This dataset contains high-resolution (~5 m) gridded estimates of belowground biomass (BGB) in the Atchafalaya and Terrebonne basins of southern Louisiana, U.S., in August 2021. The Level 3 (L3) AVIRIS-NG-derived herbaceous aboveground biomass (AGB) and necromass (AGN) Version 3 products (Jensen et al., 2025b) were used to predict the BGB. The AGB estimates were derived from the L2B BRDF-adjusted surface reflectance product (Thompson et al., 2025), following atmospheric correction to produce L2 Hemispherical-Directional surface reflectance (Thompson et al., 2018; Thompson et al., 2019). An Ordinary Least Squares Regression (OLSR) model was derived, trained on field sample measurements (n=40) of aboveground biomass (AGB), aboveground necromass (AGN), and the natural logarithm-transformed total nitrogen (N) (Castaneda-Moya and Solohin, 2022; Castaneda-Moya and Solohin, 2023). This dataset constitutes all available field samples where AGB, AGN, total N, and BGB were measured concurrently. Belowground biomass is an essential component of organic accretion but cannot be directly measured by airborne instruments. This model infers BGB from its relationships with aboveground plant mass and foliar N concentrations. This model was applied to landscape-scale maps derived from AVIRIS-NG data to estimate BGB for the August 2021 peak biomass collection period (Figure 1).
Project: Delta-X
The Delta-X mission is a 5-year NASA Earth Venture Suborbital-3 mission to study the Mississippi River Delta in the United States, which is growing and sinking in different areas. River deltas and their wetlands are drowning as a result of sea level rise and reduced sediment inputs. The Delta-X mission will determine which parts will survive and continue to grow, and which parts will be lost. Delta-X begins with airborne and in situ data acquisition and carries through data analysis, model integration, and validation to predict the extent and spatial patterns of future deltaic land loss or gain.
Related Datasets
Jensen, D.J., E. Castañeda-Moya, E. Solohin, D.R. Thompson, and M. Simard. 2025. Delta-X: AVIRIS-NG L3 Derived Herbaceous Aboveground Biomass, MRD, Louisiana, USA, V3. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2409
- This dataset provides the AVIRIS-NG-derived herbaceous AGB and necromass (AGN) Version 3 data that were used to predict the BGB.
Castañeda-Moya, E., and E. Solohin. 2022. Delta-X: Belowground Biomass and Necromass across Wetlands, MRD, LA, USA, 2021, V2. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2238
Castañeda-Moya, E., and E. Solohin. 2023. Delta-X: Aboveground Biomass and Necromass across Wetlands, MRD, Louisiana, 2021, V2. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2237
Jensen, D.J., E. Castañeda-Moya, E. Solohin, D.R. Thompson, and M. Simard. 2024. Delta-X AVIRIS-NG L3 Derived Vegetation Types, MRD, Louisiana, USA. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2352
Thompson, D.R., D.J. Jensen, J.W. Chapman, M. Simard, and E. Greenberg. 2025. Delta-X: AVIRIS-NG BRDF-Adjusted Surface Reflectance and Mosaics, MRD, LA, 2021, V3. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2355
Thompson, D.R., D.J. Jensen, J.W. Chapman, M. Simard, and E. Greenberg. 2023. Delta-X: AVIRIS-NG L2B BRDF-Adjusted Surface Reflectance, MRD, LA, 2021, V2. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2139
Related Publication
Jensen, D., E. Solohin, E. Castañeda-Moya, M. Simard, D.R. Thompson, C. Jones, A. Christensen, A. Rovai, A. Cassaway, and R. Twilley. 2025. Investigating the Contributions of Herbaceous Vegetation Biomass to Soil Accretion in Louisiana’s Coastal Deltaic Wetlands using Airborne Imaging Spectroscopy. In Process.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the NASA Earth Venture Suborbital-3 Program (grant NH17ZDA001N-EVS3).
Data Characteristics
Spatial Coverage: Atchafalaya River and Terrebonne Basins in southern Louisiana, USA
Spatial Resolution: 4.8 m
Temporal Coverage: 2021-08-20 to 2021-08-25
Site Boundaries: Latitude and longitude are given in decimal degrees.
| Site | Westernmost Longitude | Easternmost Longitude | Northernmost Latitude | Southernmost Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atchafalaya River and Terrebonne Basins | -91.593399 | -90.36072 | 29.70695 | 28.99079 |
Data File Information
This dataset contains two data files in GeoTIFF (.(tif) format that hold belowground biomass (BGB) in Mg ha-1 for the Atchafalaya and Terrebonne Basins:
ang20210820-25_bgb_Atcha_herbaceous.tif: BGB for the Atchafalaya Basin
ang20210820-25_bgb_Terre_herbaceous.tif: BGB for the Terrebonne Basin
Properties of the GeoTIFF Files
- Coordinate system: UTM zone 15N, WGS 84 datum (EPSG:32615)
- Resolution: 4.8 m
- Number of bands: 1
- No data value: -9999
Application and Derivation
Belowground biomass (BGB) is a key component of vegetation carbon stocks, and root turnover is likewise an important process contributing to soil accretion. The data estimated here are accordingly used to inform models of accretionary processes by indicating an important facet of wetland organic matter deposition. BGB estimates can be combined with AGB counterparts to assess total wetland carbon stocks (i.e., blue carbon) and to examine spatial growth patterns across the landscape.
Quality Assessment
The BGB model (Equation 1) attained an R2 of 0.53 (P = 0.006) and a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 494.6 g m-2. The inclusion of aboveground necromass (AGN) as an input variable, as opposed to solely aboveground biomass (AGB) and N, reduced the prediction error and the predicted BGB values’ bias toward the mean.
Uncertainty in the model was characterized by comparing each in situ BGB measurement to the corresponding average of the 3×3-pixel window centered on each sample location. The in situ measurements were the total BGB for 0-50 cm soil depth at each sample point. After compiling all in situ and estimated BGB values, a scatterplot and error statistics were generated for this validation dataset (Figure 2). Through validation with the in situ BGB measurements (n = 43), the BGB map (Figure 1) attained an R2 of 0.35 and a mean absolute error (MAE) of 491.9 g m-2.
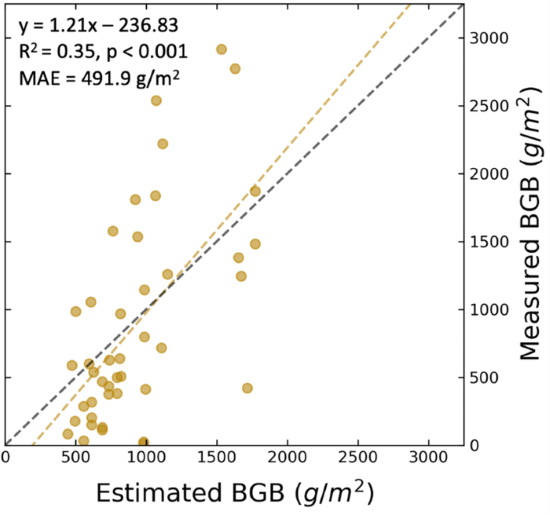
Figure 2. BGB estimates error distributions with the associated line of best fit. The validation R2 is 0.35 and the mean absolute error is 491.9 g/m2.
Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
AVIRIS-NG, the Next Generation Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer, is a pushbroom spectral mapping system with a high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) designed for high performance spectroscopy. AVIRIS-NG was developed as a successor to the Classic Airborne Visible Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS-C) (Green et al., 1998). The instrument covers the entire solar reflected spectrum from 380-2510 nm with a single Focal Plane Array (FPA), at a spectral sampling of approximately 5 nm. The AVIRIS-NG sensor has a 1 milliradian instantaneous field of view, providing altitude-dependent ground sampling distance ranging from sub-meter to 20 m scales. Its detector has a 640×480-pixel array, from which standard products are generated using the sensor’s 600 cross-track spatial samples and 425 spectral samples. Each acquisition is a “flight line” forming a continuous strip of pushbroom data that typically takes 1-10 minutes to acquire. Multiple aircraft overflights cover the region of interest in these strips, accumulating a combined map of the target area. For this campaign, AVIRIS-NG was implemented on a Dynamic Aviation King Air B200. The instrument has four components: 1) a sensor with its mount and camera glass mounted at a nadir port; 2) an onboard calibrator (OBC), mounted in the cabin next to the sensor; 3) a forward operator electronics rack; and 4) an aft thermal-control electronics rack.
Each AVIRIS-NG flightline was atmospherically corrected to produce Hemispherical-Directional surface reflectance datasets (Thompson et al., 2018; Thompson et al., 2019), followed by corrections for bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) effects and sun-glint over land and water pixels, respectively (Queally et al., 2022; Greenberg et al., 2022). The corrected pixel reflectance spectra coincident with herbaceous vegetation field samples (Castañeda-Moya and Solohin, 2023) from both Spring and Fall 2021 collections were used in concert with vegetation classification maps (Jensen et al., 2024a) to calculate AGB and AGN maps (Jensen et al., 2024b; Jensen et al., 2025b).
The methodology for estimating BGB was adapted from O’Connell et al. (2015); it incorporates estimates of foliar nitrogen (N) concentrations with our AGB and AGN maps to map BGB at the peak biomass period. Moreover, foliar N concentrations have been strongly linked with BGB and root growth rates in wetland ecosystems, particularly when combined with AGB (O’Connell et al., 2014). Foliar N was estimated from the Delta-X AVIRIS-NG spectra by applying a Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR) model, following methods outlined in O’Connell et al. (2015). Out of 84 aboveground plant samples measured for AGB and AGN, 40 had corresponding total N (mg g-1) measurements. Those concentration values served as the dependent variable in the PLSR model while the first derivative of reflectance from each sample’s coincident pixel spectrum (300 total bands used) were the independent variables. Following the PLSR process from Jensen et al. (2024b), the Predicted Residual Sum of Squares (PRESS) was calculated for a range of PLS components to determine the optimal number; five components produced the lowest residual error. The five-component derivative-based PLSR model (n=40) attained an R2 of 0.91 and a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 2.3 mg g-1. Leave-one-out cross-validation of the foliar N model showed an R2 of 0.44 and a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 5.1 mg g-1.
To estimate herbaceous BGB, a linear Ordinary Least Squares Regression (OLSR) model was trained on the field sample measurements (n=40) of AGB, AGN, and the natural logarithm-transformed total N (Castañeda-Moya and Solohin, 2022; Castañeda-Moya and Solohin, 2023). This sample set constitutes all available field samples where AGB, AGN, total N, and BGB were measured concurrently. Belowground biomass is an essential component of organic accretion but cannot be directly measured by airborne instruments. The model (Equation 3) therefore infers BGB from its relationships with aboveground plant mass and foliar N concentrations. The OLSR model is given by Equation 1:
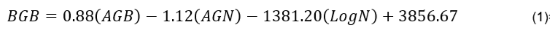
wherein AGB and AGN are expressed in units of g m-2 and N in units of mg N per g plant mass. Equation 1 was then applied to the August 2021 AVIRIS-NG-derived AGB, AGN, and N maps (with the N map ln-transformed to match the model). BGB per pixel in g m-2 was converted to Mg ha-1 for the final map and data product.
Data Access
These data are available through the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC).
Delta-X: AVIRIS-NG L3 Derived Herbaceous Belowground Biomass, MRD, LA, USA
Contact for Data Center Access Information:
- E-mail: uso@daac.ornl.gov
- Telephone: +1 (865) 241-3952
References
Castañeda-Moya, E., and E. Solohin. 2022. Delta-X: Belowground Biomass and Necromass across Wetlands, MRD, LA, USA, 2021, V2. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2238
Castañeda-Moya, E., and E. Solohin. 2023. Delta-X: Aboveground Biomass and Necromass across Wetlands, MRD, Louisiana, 2021, V2. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2237
Green, R.O., M.L. Eastwood, C.M. Sarture, T.G. Chrien, M. Aronsson, B.J. Chippendale, B.E. Faust, C.J. Pavri, M. Chovit, M. Solis, M.R. Olah, and O. Williams. 1998. Imaging Spectroscopy and the Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer AVIRIS. Remote Sensing of the Environment, 653, pp. 227-248. https://doi-org.ornl.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(98)00064-9
Greenberg, E., D.R. Thompson, D. Jensen, P.A. Townsend, N. Queally, A. Chlus, C.G. Fichot, J.P. Harringmeyer, and M. Simard. 2022. An improved scheme for correcting remote spectral surface reflectance simultaneously for terrestrial BRDF and water-surface sunglint in coastal environments. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 127:e2021JG006712. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JG006712
Jensen, D.J., E. Castañeda-Moya, E. Solohin, D.R. Thompson, and M. Simard. 2024a. Delta-X AVIRIS-NG L3 Derived Vegetation Types, MRD, Louisiana, USA. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2352
Jensen, D., D.R. Thompson, M. Simard, E. Solohin, and E. Castañeda-Moya. 2024b. Imaging spectroscopy-based estimation of aboveground biomass in Louisiana’s coastal wetlands: toward consistent spectroscopic retrievals across atmospheric states. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 129:e2024JG008112. https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JG008112
Jensen, D., E. Solohin, E. Castañeda-Moya, M. Simard, D.R. Thompson, C. Jones, A. Christensen, A. Rovai, A. Cassaway, and R. Twilley. 2025a. Investigating the Contributions of Herbaceous Vegetation Biomass to Soil Accretion in Louisiana’s Coastal Deltaic Wetlands using Airborne Imaging Spectroscopy. In Process.
Jensen, D.J., E. Castañeda-Moya, E. Solohin, D.R. Thompson, and M. Simard. 2025b. Delta-X: AVIRIS-NG L3 Derived Herbaceous Aboveground Biomass, MRD, Louisiana, USA, V3. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2409
O’Connell, J.L., K.B. Byrd, and M. Kelly. 2014. Remotely-sensed indicators of N-related biomass allocation in Schoenoplectus acutus. PLoS ONE 9:e90870. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090870
O’Connell, J.L., K.B. Byrd, and M. Kelly. 2015. A hybrid model for mapping relative differences in belowground biomass and root: Shoot ratios using spectral reflectance, foliar N and plant biophysical data within coastal marsh. Remote Sensing 712:16480–16503. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215837
Queally, N., Z. Ye, T. Zheng, A. Chlus, F. Schneider, R.P. Pavlick, and P.A. Townsend. 2022. FlexBRDF: A flexible BRDF correction for grouped processing of airborne imaging spectroscopy flightlines. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 1271:e2021JG006622. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JG006622
Thompson, D.R., V. Natraj, R.O. Green, M.C. Helmlinger, B.C. Gao, and M.L. Eastwood. 2018. Optimal estimation for imaging spectrometer atmospheric correction. Remote Sensing of Environment 216:355-373. https://doi-org.ornl.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.07.003
Thompson, D.R., K. Cawse-Nicholson, Z. Erickson, C. Fichot, C. Frankenberg, B.-C. Gao, M.M. Gierach, R.O. Green, D. Jensen, V. Natraj, and A. Thompson, A. 2019. A unified approach to estimate land and water reflectances with uncertainties for coastal imaging spectroscopy. Remote Sensing of Environment 231:111198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.05.017
Thompson, D.R., D.J. Jensen, J.W. Chapman, M. Simard, and E. Greenberg. 2023. Delta-X: AVIRIS-NG L2B BRDF-Adjusted Surface Reflectance, MRD, LA, 2021, V2. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2139
Thompson, D.R., D.J. Jensen, J.W. Chapman, M. Simard, and E. Greenberg. 2025. Delta-X: AVIRIS-NG BRDF-Adjusted Surface Reflectance and Mosaics, MRD, LA, 2021, V3. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2355