Documentation Revision Date: 2019-05-14
Dataset Version: 1
Summary
The spatial extent specifically includes the Core and Extended study areas of the Arctic Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) in Alaska and Canada plus all areas of eastern and northern Canadian provinces. The model forcing data were a temporal combination of (1) the Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR) extension for land surface hydrological modeling i.e., CFSR-Land, developed by Coccia and Wood (2018, in review) for 1979-2011 and (2) data extended to March 31, 2018 using Climate Forecast System Version 2 (CFSv2) forecast and reanalysis products.
There are 26 data files with this dataset which includes 25 data files in NetCDF (.nc4) format and the precipitation climate normal data in GeoTIFF (.tif) format.
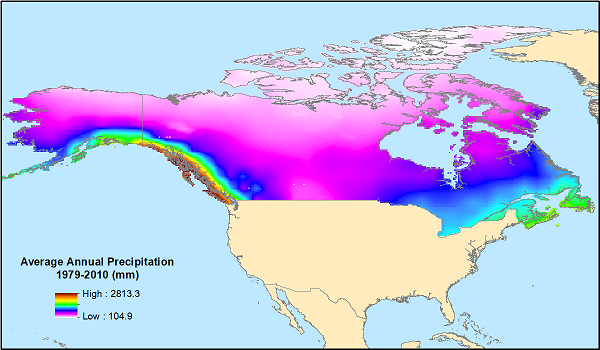
Figure 1. Average annual precipitation for 1979-2010 for the modeling domain, provided in the data file 'Precipitation_Climate_Normal_1979-2010.tif'.
Citation
Vimal, S., D.P. Lettenmaier, and L.C. Smith. 2019. ABoVE: Monthly Hydrological Fluxes for Canada and Alaska, 1979-2018. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1647
Table of Contents
- Dataset Overview
- Data Characteristics
- Application and Derivation
- Quality Assessment
- Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
- Data Access
- References
Dataset Overview
This dataset provides modeled estimates of monthly hydrological fluxes at 0.25-degree resolution over Alaska and Canada for the years 1979-2018. The estimates were derived from the Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) macroscale hydrological model version 4.1.2 with water and energy balance schemes at 0.25-degree spatial and daily temporal resolution for this 38-year period. The gridded output data products are monthly average water balance variables including precipitation (P), evapotranspiration (E), 'P minus E', evaporation, soil moisture in three soil layers, base flow and runoff, snow depth, snow water equivalent (SWE), and snow sublimation, and energy balance variables including surface temperature, albedo, latent and sensible heat flux, ground heat flux, short- and long-wave and other radiative fluxes. The daily modeled values for precipitation and evapotranspiration were also aggregated to water years and precipitation was also aggregated to a 30-year climate normal average.
The spatial extent specifically includes the Core and Extended study areas of the Arctic Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) in Alaska and Canada plus all areas of eastern and northern Canadian provinces. The model forcing data were a temporal combination of (1) the Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR) extension for land surface hydrological modeling i.e., CFSR-Land, developed by Coccia and Wood (2018, in review) for 1979-2011 and (2) data extended to March 31, 2018 using Climate Forecast System Version 2 (CFSv2) forecast and reanalysis products.
Project: Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment
The Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) is a NASA Terrestrial Ecology Program field campaign based in Alaska and western Canada between 2016 and 2021. Research for ABoVE links field-based, process-level studies with geospatial data products derived from airborne and satellite sensors, providing a foundation for improving the analysis and modeling capabilities needed to understand and predict ecosystem responses and societal implications.
Acknowledgements:
This study was funded by the NASA Terrestrial Ecology Program, ABoVE grant number NNX17AC60A
Data Characteristics
Spatial Coverage: Alaska and Canada
Spatial Resolution: 0.25 degree
Temporal Coverage: Most data cover the period 1979-01-01 to 2018-04-01. The three 'water year' files end on 2017-10-01.
Temporal Resolution: Monthly
Study Areas (All latitude and longitude given in decimal degrees)
| Site | Westernmost Longitude | Easternmost Longitude | Northernmost Latitude | Southernmost Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaska and Canada | -172.2497361 | -53.42553056 | 83.125 | 41.75075278 |
Data File Information
There are 26 data files with this dataset, including:
- 22 NetCDF files with monthly aggregations of the daily modeled output over the 471 months of the 1979-01-01 to 2018-04-01 period. Each file provides data for one model output variable.
- Three NetCDF files with "water year" aggregations of the daily modeled output over the 38 water years in the 1979-10-01 to 2017-10-01 period. Water year is defined as the 12-month period beginning on October 1. The water year is designated by the calendar year in which it ends.
- One GeoTIFF file with the '30-year climate normal' data consisting of the daily modeled output for precipitation averaged over the 30 year period 1979-2010.
No data values:
- The no data value for all files (except upward_latent_heat_flux_monthly.nc4) is zero (0).
- The no data value for upward_latent_heat_flux_monthly.nc4 is -9999. There are grid cells with data values of 0.
Spatial Data Properties
All NetCDF files have EPSG: 4326
The GeoTIFF file 'Precipitation_Climate_Normal_1979-2010.tif' has one data band, the no data value = 0, and EPSG: 4326.
Table 1. File names and Variables
| File Name | Variables | Units/format | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Balance Variables | |||
| precipitation_monthly.nc4 | OUT_PREC | kg/m2 | Precipitation |
| evapotranspiration_monthly.nc4 | EVAP | kg/m2 | Monthly evapotranspiration |
| canopy_evap_monthly.nc4 | EVAP_CANOP | kg/m2 | Net evaporation from canopy interception |
| bare_soil_evap_monthly.nc4 | EVAP_BARE | kg/m2 | Net evaporation from bare soil |
| moisture_intercept_storage_monthy.nc4 | WDEW | kg/m2 | Total moisture interception storage in canopy |
| vegetation_transpiration_monthly.nc4 | TRANSP_VEG | Kg/m2 | Net transpiration from vegetation |
| soil_moisture_monthly.nc4 | SOIL_LIQ1, SOIL_LIQ2, and SOIL_LIQ3 | kg/m2 | Soil moisture at 3 levels: top=LIQ1, middle=LIQ2, and bottom=LIQ3 |
| snow_depth_monthly.nc4 | SNOW_DEPTH | cm | Snow Depth |
| snow_water_equivalent_monthly.nc4 | SWE | kg/m2 | Snow Water Equivalent |
| net_snow_sublimation_monthly.nc4 | SUB_SNOW | kg/m2 | Total net sublimation from snowpack (surface and blowing) |
| canopy_snow_sublimation_monthly.nc4 | SUB_CANOP | kg/m2 | Net sublimation from snow stored in canopy |
| baseflow_monthly.nc4 | BASEFLOW | kg/m2 | Baseflow |
| runoff_monthly.nc4 | RUNOFF | kg/m2 | Runoff |
| Energy Balance Variables | |||
| surface_temperature_monthly.nc4 | SURF_TEMP | Degrees C | Average surface temperature |
| radiative_surface_temp_monthly.nc4 | RAD_TEMP | Degrees C | Average radiative surface temperature |
| upward_latent_heat_flux_monthly.nc4 | LATENT | W/m2 | Net upward latent heat flux |
| upward_sensible_heat_flux_monthly.nc4 | SENSIBLE | W/m2 | Net upward sensible heat flux |
| ground_heat_flux_monthly.nc4 | GRND_FLUX | W/m2 | Net heat flux into ground |
| surface_albedo_monthly.nc4 | ALBEDO | Average surface albedo (albedo as a fraction) | |
| downward_shortwave_flux_monthly.nc4 | NET_SHORT | W/m2 | Net downward shortwave flux |
| downward_radiation_flux_monthly.nc4 | R_NET | W/m2 | Net downward radiation flux |
| aerodynamic_resistance_monthly.nc4 | AERO_RESIST | m-1/s | "Scene" canopy aerodynamic resistance (tiles with overstory contribute overstory resistance; others contribute surface resistance) |
| Water Year Files | |||
| precipitation_water_year.nc4 | OUT_PREC | kg/m2 | Precipitation for the water year, 38 years |
| evapotranspiration_water_year.nc4 | EVAP | kg/m2 | Evapotranspiration for the water year, 38 years |
| precip_evapo_water_year.nc4 | P_E | kg/m2 | Precipitation minus Evapotranspiration for the water year, 38 years |
| Precipitation Climate Normal | |||
| Precipitation_Climate_Normal_1979-2010.tif | OUT_PREC | mm/year | Climate Normal (30-year average in mm/year) for the period 1979-2010 |
Application and Derivation
These data provide estimated historical climate information for the ABoVE study domain, which can be used to understand hydrological trends associated with climate change.
Quality Assessment
For validation of the data product, Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) gauges, ECCC climate normal (1981-2010), and station based gridded data CRU.TS.4.01 (Harris et al., 2014) were used. Evaluation of the data product for regional and seasonal biases showed that in higher elevations there is a positive bias, especially in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Yukon, and Alaska, but considering the domain-wide region, the data product agrees well with the recent climate normal (1981-2010) published by ECCC. Seasonal bias was found to be negligible across all regions.
Known problems that may limit use:
- Some missing points (gaps) were filled with nearest neighbor interpolation.
- The monthly mean quantile values of Precipitation, Wind Speed and Temperature for the period 2011-2018 were mapped to match the quantile values of the reference period 1979-2010.
- Modeled evaporation does not account for lakes, and this may represent a significant amount of evaporation. An update to the data product including explicit lake characterization will be released in 2019.
Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
The Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) model, a macroscale hydrologic model that solves full water and energy balances (Liang et al., 1994) over a gridded land surface, was used for data simulations.
The model forcing data were derived from a combination of (1) Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR) extension for land surface hydrological modeling i.e., CFSR-Land, developed by Coccia and Wood (2018, in review) for the time period 1979-2011. CFSR-Land is an extension of the Sheffield et al. (2006) dataset, which constitutes global meteorological forcing for land surface models. And, (2) Climate Forecast System Version 2 (CFSv2) products were used to extend the data to March 31, 2018. CFSv2 includes an upgraded four-level soil model, an interactive three-layer sea ice model, and historically prescribed (i.e., rising) CO2 concentrations (Saha et al., 2014). Monthly means were matched with CFSR-Land by quantile mapping at the monthly scale. The number of rain days were also corrected to match CFSR-Land.
The Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) macroscale hydrological model version 4.1.2 with water and energy balance schemes was run at 0.25 degree spatial resolution and daily temporal resolution. The data product produced included gridded files (netcdf) of several water balance variables such as precipitation (P), evapotranspiration (E), P-E, soil moisture in 3 soil layers, snow depth, snow water equivalent, etc. and energy balance variables such as albedo, latent heat, short- and long-wave and other radiative fluxes.
Data Access
These data are available through the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC).
ABoVE: Monthly Hydrological Fluxes for Canada and Alaska, 1979-2018
Contact for Data Center Access Information:
- E-mail: uso@daac.ornl.gov
- Telephone: +1 (865) 241-3952
References
Harris, I., P. D. Jones, T. J. Osborn, and D. H. Lister. 2014. “Updated High-Resolution Grids of Monthly Climatic Observations – the CRU TS3.10 Dataset.” International Journal of Climatology 34 (3): 623–42. https://doi.org/ 10.1002/joc.3711
Coccia, G., Wood, E., 2018. CFSR-Land: a new High Temporal Resolution Global Land Data Assimilation Product (in review).
Liang, X., D. P. Lettenmaier, E. F. Wood, and S. J. Burges, 1994: A Simple hydrologically Based Model of Land Surface Water and Energy Fluxes for GSMs, J. Geophys. Res., 99(D7), 14,415-14,428. https://doi.org/10.1029/94JD00483
Saha, S., S. Moorthi, X. Wu, J. Wang, S. Nadiga, P. Tripp, D. Behringer, Yu-T. Hou, M. Iredell, M. Ek, J. Meng, R. Yang, M.P. Mendez, H. van den Dool, Q. Zhang, W. Wang, M. Chen, and E. Becker. 2014. “The NCEP Climate Forecast System Version 2.” Journal of Climate 27 (6): 2185–2208. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00823.1