Get Data
Summary
This data set contains atmospheric chemistry and meteorological data from the NASA Transport and Atmospheric Chemistry near the Equator-Atlantic (TRACE-A) field study. The NASA TRACE-A study took place in August 1992 to determine the cause and source of high concentrations of ozone that accumulate over the Atlantic ocean between southern Africa and South America during the months of August through October.
The processed, quality controlled and integrated data in the documented Pre-LBA Data sets were originally published as a set of three CD-ROMs (Marengo and Victoria, 1998) but have now been archived individually.
Pre-LBA Data Set Collection Initiative
The Pre-LBA data set collection was dedicated to providing information to the LBA research community about existing data that have been collected in Amazonia during the 20 years prior to 1998. The main goal of this activity was to compile and document existing data sets in a consistent manner and make them available prior to the beginning of the LBA experiment.
The data set compilation efforts included satellite imagery, micrometeorological observations, near surface and upper-air atmospheric conditions, surface biophysical and hydrological measurements obtained from 1970s-1990s in a number of field experiments. Data were collected for several intensive field campaigns, during the rainy and dry seasons, and other periods that vary from short intensive field campaigns to several years worth of observations, measured sometimes with a time resolution of 5 minutes and 1 hour.
Data Citation:
Cite this data set as follows:
Artaxo, P., V.W. J.H. Kirchhoff, E.B. Pereira, R.C.S. Alvala. 2009. Pre-LBA TRACE-A Data. Data set. Available on-line [http://daac.ornl.gov] from Oak Ridge National Laboratory Distributed Active Archive Center, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, U.S.A. doi:10.3334/ORNLDAAC/920
The original CD-ROM citation is as follows:
Marengo, J.A., and R.L. Victoria. 1998. Pre-LBA Data Sets Initiative, 3 vols. [Pre-Large-Scale Biosphere-Atmosphere Experiment in Amazonia Data Sets Initiative, 3 vols.].CD-ROM. Centro de Previsao de Tempo e Estudios Climaticos, Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (CPTEC/INPE) [Center for Weather Forecasting and Climate Study, National Institute for Space Research], Sao Paulo, Brazil.
|
Pre-LBA Data Set Collection Metadata Campaign: TRACE-A Transport and Atmospheric Chemistry Experiment - A Keywords OZONE BIOMASS BURNING NITROGEN OXIDES DC-8 AIRCRAFT STRATOSPHERE Investigators Last_name: Artaxo First_name: Paulo Email: artaxo@if.usp.br Phone: +55-11-818.7016 Phone: +55-11-818.6925 Address: Instituto de Fisica-USP Caixa Postal 66318 Zip code: 05389-970 City: Sao Paulo State_or_Province: Sao Paulo Country: Brazil Last_name: Kirchhoff First_name: Volker Middle_name: W.J.H. Email: kir@spd.inpe.br Phone: +55-12-325.6037 FAX: +55-12-322.9887 Address: INPE Av. dos Astronautas, 1758 C.P.515 Zip code: 12201-970 City: Sao Jose dos Campos State_or_Province: Sao Paulo Country: Brazil Last_name: Pereira First_name: Enio Middle_name: Bueno Email: enio@das.inpe.br Phone: +55-12-321.3029 Phone: +55-12-321.6969 Address: INPE Av. dos Astronautas, 1758 C.P.515 - Zip code:01201-970 City: Sao Jose dos Campos State_or_Province: Sao Paulo Country: Brazil Last_name: Alvala First_name: Regina Middle_name: C.S. Email: regina@met.inpe.br Phone: +55-12-325-6644 FAX: +55-12-325-6666 Address: INPE Av. dos Astronautas, 1758 C.P.515 - zip code : 12201-970 City: Sao Jose dos Campos State_or_Province: Sao Paulo Country: Brazil Technical_Contact Last_name: Kirchhoff First_name: Volker Middle_name: W.J.H. Email: kir@spd.inpe.br Phone: +55-12-325.6037 FAX: +55-12-322.9887 Address: INPE Av. dos Astronautas, 1758 C.P.515 Zip code: 12201-970 City: Sao Jose dos Campos State_or_Province: Sao Paulo Country: Brazil Start_Date: 1992-08-18 Stop_Date: 1992-10-26 |
Coverage Southernmost_latitude: -40 Northernmost_latitude: -4 Westernmost_longitude: -125 Easternmost_longitude: 40 Minimum_altitude: Surface Maximum_altitude: 10km Location: South America and Southern Africa Data_Resolution Latitude_Resolution:9S Longitude_Resolution:49W Altitude_Resolution: Surface Author Last_name: Nobre First_name: Carlos Middle_name: A. Email: nobre@cptec.inpe.br Phone: +55 12 561 2822 FAX: +55 12 561 2835 Address: CPTEC-INPE Rodovia Presidente Dutra, Km 40 C. P.01 - Zip code 12630-000 City: Cachoeira Paulista State_or_Province: Sao Paulo Country: Brazil Data_CenterData_Center Data_Center_Name: INPE, AEB, NASA Data_Center_URL: http://www.cptec.inpe.br/lba/prelba/prelba.html Dataset_ID: SCAR-B Dataset_ID: TRACE-A Data_Center_Contact Last_name: Kirchhoff First_name: Volker Middle_name: W.J.H. Email: plinio@dge.inpe.br Phone: +55-12-325.6037 FAX: +55-12-322.9887 Address: INPE Av. dos Astronautas, 1758 C.P.515 Zip code: 12201-970 City: Sao Josi dos Campos State_or_Province: Sao Paulo Country: Brazil Constraints Access: Data may not be used for commercial applications. Use: Data may not be used for commercial applications. |
Data Description
Data and images for TRACE-A measurements for both Africa and South America are included in the archived data. Users must select data for flights and areas of interest. Each TRACE-A Data Source entry has a corresponding compiled and compressed data file. Images are provided as companion files.
| Data Type | TRACE-A Data Source(Each entry has a corresponding compiled and compressed file.) | TRACE-A Data Type | TRACE-A Data Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| DATA | NASA DC8 AIRCRAFT measurement data. (NASA_DC-8_AIRCRAFT.zip)
| AIRCRAFT | ANDERSON: CO2 BRADSHAW: Nitrogen Oxides BROWELL: UV Aerosol Scattering Tropopause heights and ozone columns GREGORY: Ozone/Aerosols HEIKES: Formaldehyde PROJECT: Nav/Met Data ROWLAND: Hydrocarbons SACHSE: CO, CH4, and N2O SINGH: Acetone and Ethanol TALBOT: Acidic Trace Gases |
| BRAZIL (BRAZIL.zip) |
AIRCRAFT | Trace Gasses | |
| FIRECOUNT | Weekly Total Pixel Fire Counts/AVHRR | ||
| RAWINSONDES | Rawinsondes | ||
| FUNCEME (FUNCEME.zip) | AIRCRAFT | Met, Aerosol, and Radiation | |
| GROUND (GROUND.zip) |
ASCENSION | Ozone sonde | |
| CUIABA | Ozone sonde | ||
| FUELBERG | Kinematic Parcel Trajectory | ||
| NATAL | Ozone sonde | ||
| PORTO | Ozone sonde | ||
|
SATELLITE (TOMS_SATELLITE.zip) |
SATELLITE | TOMS/NIMBUS-7 | |
|
IMAGE companion files |
BRAZIL |
SATELLITE | Weekly Total Pixel Fire Count Images |
| PLOTS (PLOTS_IMAGES.zip) |
AIRCRAFT | DC-8 Flight Trajectories | |
| SATELLITES (NOAA_IMAGES.zip) | SATELLITE | NOAA satellites 10, 11, and 12 - Channels 2 and 4 |
TRACE-A Background
A pool of ozone was initially discovered in the mid 1980s as a result of the re-analysis of ozone measurements from two operational satellites using a newly developed mathematical technique to extract the concentration of ozone in the troposphere. The satellite data provided the first hints of ozone spread over thousands of square kilometers over the Atlantic Ocean at concentrations comparable to those found in many large cities around the world during the summertime. The fact that the enhanced levels of ozone over the Atlantic were observed to be the highest during the southern hemisphere's springtime, a period of intense burning of vegetation in both southern Africa and South America, suggested a link between the biomass burning and the ozone pollution. As additional satellite data were analyzed an alternative source was suggested to be the downward transport of ozone from the stratosphere linked to a sinking motion of air prevalent over the region during the southern hemispherical springtime.
The TRACE-A mission brought together a multi-year series of ground based and balloon measurements, aircraft measurements over Brazil, southern Africa, and the Atlantic ocean, and powerful computer models of the tropical atmosphere. TRACE-A was a cooperative project between NASA and the Brazilian Space Agency (INPE), involving over 200 scientists from US, Brazil and South Africa. The center piece of TRACE-A was the NASA DC-8 flying laboratory based at the NASA Ames Research Center. During TRACE-A, the DC-8 aircraft flew over 70,000 miles from bases in Brasilia, Brazil, Johannesburg, South Africa, Windhoek, Namibia, and Ascension Island, UK. The DC-8 was instrumented with state-of-the-art instruments for measurements of ozone and other gases that are associated with the production of ozone in the atmosphere. Two INPE aircraft from San Jose dos Campos, provided additional measurements over Brazil. Data and images from TRACE-A observations for both SA and A are included in this data set (Figure 1).
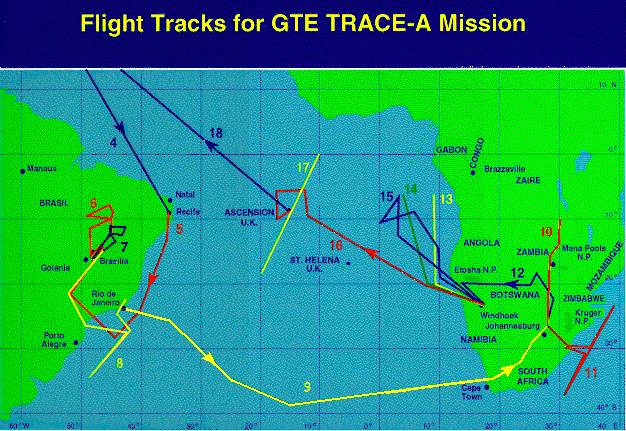
Figure 1. Flights of NASA DC-8 during TRACE-A.
During TRACE-A, another comprehensive experiment, called SAFARI (Southern African Fire-Atmosphere Research Initiative) conducted by a team of European, African, and North American scientists, studied the African fires to understand exactly what kind of vegetation burns and how this material is transformed into the air pollution pall that hangs over vast regions of South Africa, Zimbabwe, Zambia, Namibia, and Botswana during the burning season.
The picture that emerges from TRACE-A together with SAFARI, is that widespread biomass burning in both South America and southern Africa is the dominant source of the initial pollutants that lead to the formation of the high amounts of ozone over the South Atlantic Ocean. Additionally, the air motion in this part of the world is favorable for the accumulation of these pollutants over the Atlantic Ocean where the intense sunlight can do its work in transforming them into ozone and other pollution gases. The production of ozone occurred over thousands of miles and was usually the greatest at altitudes between 15,000 to 50,000 feet where relatively high concentrations of nitrogen oxides, which are needed for the production of ozone, were also measured during TRACE-A.
Results from the TRACE-A mission clearly demonstrated that the cause and source of the seasonally enhanced pool of ozone pollution over the South Atlantic Ocean is due to burning of vegetation on a massive scale in southern Africa and South America, combined with an enormous stagnation region between the two continents. What remains unclear is the source of the high concentrations of nitrogen oxides also observed by instruments aboard the DC-8 aircraft. Transport from surface sources as well as production by lightning have been suggested as the two majors sources for the high concentrations of nitrogen oxides.
Measurements of wide spread ozone plumes during the more recent (e.g. September, 1996) NASA Pacific exploratory Mission in the south tropical Pacific Ocean (PEM-Tropics) provide additional evidence of the impact that biomass burning is having on the global atmosphere.
References
Anderson B.E., W. B. Grant, G. L. Gregory, E. V. Browell, J. E. Collins,
Jr., G. W. Sachse, D. R. Bagwell, C.H. Hudgins, D. R. Blake, and N. J. Blake,
Aerosols from biomass burning over the tropical south Atlantic region:
Distributions and impacts. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30,
1996, pp. 24117-24138.
doi:10.1029/96JD00717
Bradshaw, J. D. and S. T. Sandholm, Airborne measurments of NO, NO2, and NOy as related to NASA's TRACE-A field program: Final Report, April 1, 1992-June 30, 1995, NASA CR-199253, 8 p.
Browell E. V., M. A. Fenn, C. F. Butler, W. B. Grant, M. B. Clayton, J. Fishman, A. S. Bachmeir, B. E. Anderson, G. L. Gregory, H. E. Fuelberg, J. D. Bradshaw, S. T. Sandholm, D. R. Blake, B. G. Heikes, G. W. Sachse, H. B. Singh, and R. W. Talbot, Ozone and aerosol distributions and air mass characteristics over the South Atlantic basin during the burning season. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp.24043-24068. doi:10.1029/95JD02536
Fishman, J., V.G. Brackett, E.V. Browell, and W.B. Grant, Tropospheric ozone derived from TOMS/SBUV measurements during TRACE-A. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24069-24082. doi:10.1029/95JD03576
Andreae, M. O. , J. Fishman, M. Garstang, J.G. Goldammer, C. O. Justice, J. S. Levine, R. J. B. J. Stocks, A. M. Thompson, B. van Wilgen and the STARE/TRACE- A/SAFARI-92 Science Team,Biomass burning in the global vironment: First results from the IGAC/BIBEX field campaign STARE/TRACE-A/SAFARI-92. Global Atmospheric-Biospheric Chemistry, Prinn(ed.), Plenum Press, New York, 1994, pp.83- 101, presented at First Scientific Conference of IGAC, Eilat, Israel, April 18-22,1993.
Jacob, D.J., B. G. Heikes, S. -M. Fan, J. A. Logan, D. L. Mauzerall, J. D.
Bradshaw, H. B. Singh, G. L. Gregory, R. W. Talbot, D. R. Blake, and G.W. Sachse,
Origin of ozone and NOx in the tropical troposphere: A photochemical analysis of
aircraft observations over the South Atlantic basin. J. Geophys. Res.,Vol. 101,
No. D19,October 30, 1996, pp. 24235-24250.
doi:10.1029/96JD00336
Andreae, M. O., J. Fishman, and J. Lindesay, The Southern Tropical Atlantic
Region Experiment(STARE): Transport and Atmospheric Chemistry near the Equator-
Atlantic(TRACE-A) and Southern African Fire-Atmosphere Research
Initiative(SAFARI): An Introduction. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19,
October 30, 1996, pp. 23519- 23520.
doi:10.1029/96JD01786
Kirchhoff, V.W.J.H., J.R. Alves, F.R. da Silva, and J. Fishman, Observations of ozone concentrations in the Brazilian cerrado during the TRACE-A field expedition. J.Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24029-24042.doi:10.1029/95JD03030
Kirchhoff, V.W.J.H., and P.C. Alvala, Overview of an aircraft expedition into the Brazilian cerrado for the observation of atmospheric trace gases. J. Geophys. Res., Vol.101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 23973-23982. doi:10.1029/95JD03029
Kirchhoff, V. W. J. H., C. A. Nobre, E. B. Pereira, E. V. A. Marinho, A. Souza, H.G. Pavo, E. D. Freire, V. Silva, I. M. O. Silva, J. Marques, V. Casseti, M. H. Santos, S.Guimares, and L. M. Coutinho, TRACE-A Brazil: Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop.Brazilian Journal of Geophysics, Vol. 10, No. 1, July 1992, pp. 65-81.
Pickering, K.E., A. M. Thompson, Y. Wang, W. -K. Tao, D. P.McNamara, V. W.J. H. Kirchhoff, B. G. Heikes, G. W. Sachse, J. D. Bradshaw, G.L. Gregory, and D. R.Blake, Convective transport of biomass burning emissions over Brazil during TRACE-A. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 23993-24012. doi:10.1029/96JD00346
Pereira, E.B., A.W. Setzer, F. Gerab, P.E. Artaxo, M.C.Pareira, and G. Monroe, Airborne measurements of biomass burning aerosols in Brazil related to the TRACE-A experiment. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 23983-23992. doi:10.1029/96JD00098
Talbot, R.W., J. D. Bradshaw, S. T. Sandholm, S. Smyth, D.R. Blake, N. J.
Blake,G. W. Sachse, J. E. Collins, Jr., B. G. Heikes, B. E. Anderson, G. L.
Gregory, H. B. Singh, B. L. Lefer, and A. S. Bachmeir, Chemical characteristics
of continental outflow over the tropical south Atlantic Ocean from Brazil and
Africa. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24187-24202.
doi:10.1029/95JD03630
Additional References
Bachmeier, A.S., and H.E. Fuelberg, A meteorological overview of the TRACE-A period. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 23881-23888.
Bartlett, K.B., G.W. Sachse, J.E. Collins, Jr., and R.C. Harriss, Methane in the tropical South Atlantic: Sources and distribution during the late dry season. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24139-24150.
Blake, N. J., D. R. Blake, J. E. Collins, Jr., G. W. Sachse, B. E. Anderson, J. A. Brass, P. J. Riggan, and F. S. Rowland, Biomass burning emissions of atmospheric methyl halide and hydrocarbon gases in the south Atlantic region. Biomass Burning and Global Change, ed. J. S. Levine, MIT Press, 1996, Vol. 2, Chap. 56, pp.575-594.
Blake, N. J., D. R. Blake, B. C. Sive, T. -Y. Chen, F. S. Rowland, J. E. Collins, Jr., G. W. Sachse, and B. E. Anderson, Biomass burning emissions and vertical distribution of atmospheric methyl halides and other reduced carbon gases in the South Atlantic region. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24151-24164.
Carroll, M. A. and L. Emmons, Data archive for NOy from observations and construction and testing of airborne instrument for simultaneous measurments of NO, NO2, NOy, and O3-Final Report, January 1, 1994-December 31, 1995. Univ. of Michigan, December 1995, NASA CR-200086, 34 p.
Chatfield, R. B., J. A. Vastano, H. B. Singh, and G. W. Sachse, A general model of how fire emissions and chemistry produce Africian/oceanic plumes(O3, CO, PAN, smoke) in TRACE A. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp.24279-24306.
Collins, Jr., J.E., B.E. Anderson, G.W.Sachse, J.D.W.Barrick, L.O. Wade, L.G. Burney, and G.F. Hill, Atmospheric fine structure during GTE/TRACE A: Relationships between ozone, carbon monoxide, and water vapor. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24307-24316.
Cros, B., D. Nganga, A. Minga, J. Fishman, and V. Brackett, The Distribution of tropospheric ozone at Brazzaville, Congo determined from ozonesonde measurements. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 97, No. D12, August 20, 1992, pp. 12,869-12,875.
Fishman, J., Experiment probes elevated ozone levels over the tropical south Atlantic Ocean. AGUEOS Transactions, Vol. 75, No. 33, August 16, 1994, pp. 380-381.
Fishman, J., B. E. Anderson, E. V. Browell, G. L. Gregory, G. W., Sachse, V. G. Brackett, and K. M. Fakhruzzaman, The tropospheric ozone maximum over the tropical south Atlantic Ocean: A meteorological perspective from TRACE-A. AMS Conference on Atmospheric Chemistry (pre-print volumn), Nashville, TN, January 23-28, 1994, pp. 253-260.
Fishman, J., V. G. Brackett, and K. Fakhruzzaman, Distribution of tropospheric ozone in the tropics from satellite and ozonsonde measurements. J. Atmos. Terrestrial Physics, Vol. 54, No. 5, May, 1992, pp. 589-597.
Fishman, J., J.M. Hoell, Jr., R.J. Bendura, R. J. McNeal, and V.W.J.H. Kirchhoff, NASA GTE TRACE-A experiment (September-October, 1992): Overview. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19,October 30, 1996, pp. 23865-23880.
Fuelberg, H.E., J.D. VanAusdall, E.V. Browell, and S.P. Longmore, Meteorological conditions associated with vertical distributions of aerosols off the west coast of Africa. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24105-24116.
Fuelberg, H.E., R. O. Loring, Jr., M. V. Watson, M. C. Sinha, K. E. Pickering, A. M. Thompson, G. W. Sachse, D. R. Blake, and M. R. Schoeberl, TRACE-Atrajectory intercomparison: 2, Isentropic and kinematic methods. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 23927-23939.
Garstang, M., P. D. Tyson, E. V. Browell, and R. J. Swap,Large-scale transports of biogenic and biomass burning products. in Biomass Burning and Global Change, ed. by J. S. Levine, Chapter 37, MIT Press, 1996, pp. 389-395.
Grant, W. B., Tropical stratospheric ozone changes following the eruption of Mount Pinatubo. in G. Fiocco, D. Fua and G. Visconti, eds., The Mount Pinatubo Eruption Effects on the Atmosphere and Climate, NATO ASI Series, Vol. I, No. 42, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1996, pp.161-175
Grant, W. B., E. V. Browell, J. Fishman, V. G. Brackett, R.E. Veiga, D. Nganga,A. Minga, B. Cros, C. F. Butler, M. A. Fenn, C. S. Long, and L.L. Stowe, Aerosol-associated changes in tropical stratospheric ozone following the eruption of Mt. Pinatubo, J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 99, No. D4, April 20,1994, pp. 8197-8211.
Grant, W. B., J., Fishman, E. V. Browell, V. G. Brackett,D. Nganga, A. Minga, B.Cros, R. E. Veiga, C. F. Butler, M. A. Fenn, and G. D. Nowicki,Observations of reduced ozone in the tropical stratosphere after the eruption of Mt. Pinatubo. Geophys. Res. Ltrs., Vol. 19, No. 11, June 2, 1992, pp. 1109-1112.
Gregory, G.L., H.E. Fuelberg, S.P. Longmore, B.E. Anderson, J.E. Collins, Jr. and D.R. Blake, Chemical characteristics of tropospheric air over the tropical South Atlantic Ocean: Relationship to trajectory history. J. Geophys.Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 23957-23972.
Gregory, G. L. and A. D. Scott, Jr., Compendium of NASA Data Base for the Global Tropospheric Experiment's Transport and Atmospheric Chemistry near the Equator-Atlantic (TRACE-A). NASA Technical Memorandum 110151,April 1995,162 p.
Heikes, B. G., M. Lee, D. Jacob, R. Talbot, J. D. Bradshaw,H. B. Singh, D. R.Blake, B. E. Anderson, H. Fuelberg, and A. M. Thompson, Ozone,hydroperoxides,oxides of nitrogen, and hydrocarbon budgets in the marine boundary layer over the South Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24221-24234.
Kim, J. H., R. D. Hudson, and A. M. Thompson, A new method of deriving time-averaged tropospheric column ozone over the tropics using total ozone mapping spectrometer (TOMS) radiances: Intercomparison and analysis using TRACE-A data. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24317-24330.
Krishnamurti, T. N., H. E. Fuelberg, M. C. Sinha, D.Oosterhof, E. L. Bensman, and V. B. Kumar, The meteorological environment of the tropospheric ozone maximum over the tropical south Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res., Vol.98, No. D6, June 20, 1993, pp. 10621-10641.
Krishnamurti, T.N., M.C. Sinha, M. Kanamitsu, D. Oosterhof, H. Fuelberg, R.Chatfield, D.J. Jacob, and J. Logan, Passive tracer transport relevant to the TRACE-A experiment. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 23889-23908.
Loring, Jr., R.O., H.E. Fuelberg, J. Fishman, M. V. Watson, and E.V. Browell, Influence of middle-latitude cyclone on tropospheric ozone distributions during a period of TRACE A. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 23941-23956. (originally published as Loring's M. S. thesis at Florida State University in 1995).
Nganga, D., A. Minga, B. Cros, C. B. Biona, J. Fishman, and W.B. Grant, The vertical distribution of ozone measured at Brazzaville, Congo during TRACE-A. J.Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp.24095-24104.
Olson, J. R., A study of the mass transport of enhanced continental ozone in the tropics and its impact over the remote southern Atlantic ocean.AGU Chapman Conference, Williamsburg, VA, March 13-17, 1995, also Chapter 18 in Biomass Burning and Global Change, ed. J. S. Levine, MIT Press, 1996.
Olson, J.R., J. Fishman, V.W.J.H. Kirchhoff, D. Nganga, and B. Cros, Analysis of the distribution of ozone over the southern Atlantic Ocean. J.Geophys. Res., Vol. 101,No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24083-24094.
Pickering, K.E., A.M. Thompson, D.P. McNamara, M.R. Schoeberl, H.E. Fuelberg, R.O. Loring, Jr., M.V. Watson, K. Fakhruzzaman, and A.S.Bachmeier, TRACE-A trajectory intercomparison: 1, Effects of different input analyses. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 23909-23926.
Singh, H. B., D. Herlth, R. Kolyer, R. Chatfield, W.Viezee, L. J. Salas, Y. Chen, J. D. Bradshaw, S. T. Sandholm, R. Talbot, G. L. Gregory, B. E. Anderson, G. W. Sachse,E. V. Browell, A. S. Bachmeir, D. R. Blake, B. G. Heikes, D. J.Jacob, and H. E. Fuelberg, Impact of biomass burning emissions on the comparison of the south Atlantic troposphere: Reactive nitrogen and ozone. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24203-24220.
Smyth, S, S. T. Sandholm, J. D. Bradshaw, R. W. Talbot, D.R. Blake, N. J. Blake, F. S. Rowland, H. B. Singh, G. L. Gregory, B. E. Anderson, G.W. Sachse, J. E. Collins, Jr., and A. S. Bachmeir, Factors influencing the upper free tropospheric distribution of reactive nitrogen over the south Atlantic during the TRACE-A experiment. J. Geophys.Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24165-24186.
Thompson, A.M., Model evaluation of biomass burning effects on tropical ozone and oxidizing capacity: Overview and examples from SAFARI-92/TRACE-A. AGU Chapman Conference Williamsburg, VA., March 13-17, 1995, also in Biomass Burning and Global Change, ed. by J. Levine, MIT Press, 1996.
Thompson, A. M., D. P. McNamara, K. E. Pickering, and R. D. McPeters, Effect of marine stratocumulus on TOMS ozone. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 98, Number D12, December 20, 1993, pp.23051-23058.
Thompson, A.M., K. E. Pickering, D. P. McNamara, M. R. Schoeberl, R. D. Hudson, J. H. Kim, E. V. Browell, V. W. J. H. Kirchhoff, and D. Nganga, Where did tropospheric ozone over southern Africa and the tropical Atlantic come from in October 1992? Insights from TOMS, GTE/TRACE-A and SAFARI 1992. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24251-24278.
Tyson, P. D., M. Garstang, R. J. Swap, E. V. Browell, R. D. Diab, and A. M. Thompson, Transport and vertical structure of ozone and aerosol distributions over southern Africa. in Biomass Burning and Global Change, ed. by J. S. Levine, Chapter 39, MIT Press, 1996, pp. 403-421.
Wang, Y., W. -K. Tao, K.E. Pickering, A.M. Thompson, J. S. Kain, R.F. Adler, J. Simpson, P.R. Keehn, and G.S. Lai, Mesoscale model simulations of TRACE-A and Preliminary Regional Experiment for Storm-Scale Operational and Research Meteorology convective systems and associated tracer transport. J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, No. D19, October 30, 1996, pp. 24013-24028.
Watson, M. V., An examination of tropospheric ozone distributions over the western Indian Ocean during TRACE-A. M. S. thesis, Florida State University, Tallahassee, 1996, 71pp. (available from H. E. Fuelberg, Dept. of Meteorology, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL 32306).
Data Access:
This data is available through the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC) [http://daac.ornl.gov].
Data Archive Center:
Contact for Data Center Access Information:
E-mail: uso@daac.ornl.gov
Telephone: +1 (865) 241-3952