Documentation Revision Date: 2023-08-23
Dataset Version: 2.1
Summary
Five data files are distributed with this dataset: (1) a shapefile (compressed as .zip) with a vector representation of the Core and Extended study regions, (2) one shapefile (compressed as .zip), for the 240, 30, and 5-meter spatial resolution nested Standard Reference Grids, (3) grid data provided in .kmz format, (4) a GeoTIFF file that is a raster representation of the Core and Extended study regions at 1,000-meter pixel resolution, and (5) one NetCDF file of the core and extended study regions for use with the International Land Model Benchmarking (ILAMB) modeling environment.
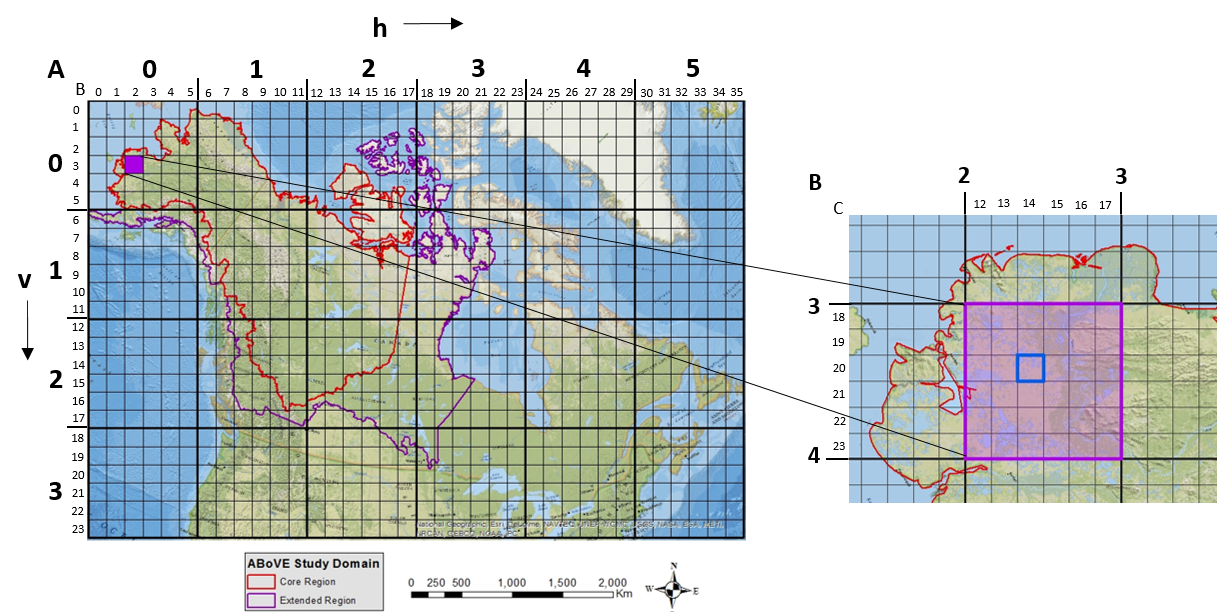
Figure 1. ABoVE spatial data products - the Study Domain with Core and Extended study regions displayed and the Standard Reference Grid showing the nested 240 meter, 30 meter and 5-meter tiling scheme. Left: The location of sample tile Bh002v003 (in purple) within both the larger A grid (in bold) and the smaller B grid. Right: The location of sample tile Ch014v020 within the larger two grids is shown.
Citation
Loboda, T.V., and M.L. Carroll. 2023. ABoVE: Study Domain and Standard Reference Grids, Version 2. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1527
Table of Contents
- Dataset Overview
- Data Characteristics
- Application and Derivation
- Quality Assessment
- Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
- Data Access
- References
- Dataset Revisions
Dataset Overview
The Arctic - Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) has developed two standardized spatial data products to expedite coordination of research activities and to facilitate data interoperability. The ABoVE Study Domain encompasses the Arctic and boreal regions of Alaska, USA, and the western provinces of Canada, North America. Core and Extended study regions have been designated within this Domain and are provided in both a vector representation (Shapefile) and a raster representation (GeoTIFF at 1,000-meter spatial resolution). A Standard Reference Grid System has been developed to cover the entire Study Domain and also extends to the eastern portion of North America. This Reference Grid is provided as nested polygon grids at scales of 240, 30, and 5-meter spatial resolution. The 5-meter grid is new in Version 2.
Note that the designated standard projection for the all ABoVE products is the Canadian Albers Equal Area projection.
Project: Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE)
The Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) is a NASA Terrestrial Ecology Program field campaign based in Alaska and western Canada between 2016 and 2021. Research for ABoVE links field-based, process-level studies with geospatial data products derived from airborne and satellite sensors, providing a foundation for improving the analysis and modeling capabilities needed to understand and predict ecosystem responses and societal implications.
The ABoVE Study Domain encompasses the Arctic and boreal regions of Alaska, USA, and the western provinces of Canada, North America. Core and Extended study regions have been designated within this Domain. The Core Region encompasses a range of landscapes, with areas that are rapidly changing in complex ways in response to global-scale climate change as well as regional-scale disturbances, and others that are not. This combination will allow for studies of both vulnerability and resilience. The Extended Region, outside of the Core Region, is needed for study of a subset of important changes that are unique to these regions (for example, insect outbreaks and forest dieback in the southern boreal forest). The Extended Region provides additional opportunities for research where environmental conditions are considered to be antecedent to those in the Core Region, as well collaboration on research being sponsored by partners.
The domain for the ABoVE study area is over 6.3 x 106 km2. Within the ABoVE campaign, many thematic data products will be generated from field measurements, flux towers, airborne remote sensors and satellite remote sensing data. The data sets will range considerably in resolution, format, geographic extent, projection and/or reference system.
The standardized Reference Grid and projection will enable researchers to identify, align and subdivide data products in order to facilitate archiving and distribution of datasets (both for long-term archiving of the data and near-term use throughout the campaign’s duration), and simplifies data standardization for scientific analysis within ABoVE.
Data Characteristics
Spatial Coverage: Boreal and Tundra regions of North America -- covering all of Alaska and all provinces of Canada
Spatial Resolution: Varied
Temporal Coverage: 2014-01-01 to 2023-04-20
Temporal Resolution: Not Applicable
Study Area: All latitude and longitude given in decimal degrees
| Site (Region) | Westernmost Longitude | Easternmost Longitude | Northernmost Latitude | Southernmost Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABoVE Study Domain | -176.124747 | -66.917776 | 81.608577 | 39.415027 |
| Standard Reference Grid (all grids) | -177.469005 | -16.792179 | 82.484024 | 34.058481 |
| ABoVE Study Domain for ILAMB (NetCDF file) | -180 | 180 | 90 | -90 |
Data File Information:
Five data files are distributed with this dataset: (1) a shapefile (compressed as .zip) with a vector representation of the Core and Extended study regions, (2) one shapefile (compressed as .zip), for the 240, 30, and 5-meter spatial resolution nested Standard Reference Grids, (3) grid data provided in .kmz format, (4) a GeoTIFF file that is a raster representation of the Core and Extended study regions at 1,000-meter pixel resolution, and (5) one NetCDF file with the of the core and extended study regions for use with the ILAMB modeling environment.
File Names and Descriptions
| File name | Description |
|---|---|
| ABoVE_Study_Domain.zip | Core and Extended study regions. When unzipped, the file provides the shapefile ABoVE_Study_Domain.shp |
| ABoVE_240m_30m_5m_grid_tiles.zip | ABoVE reference grid for the three spatial resolutions. When unzipped, the file provides the shapefile ABoVE_240m_30m_5m_grid_tiles.shp. |
| ABoVE_240m_30m_5m_grid_tiles.kmz | ABoVE reference grid for the three spatial resolutions. |
| ABoVE_Study_Domain.tif | ABoVE Study Domain as a raster file. This file provides a raster representation of the core and extended ABoVE study domain. |
| ABoVE_Study_Domain_ILAMB.nc | One NetCDF file of the Core and Extended study regions at a 0.5-degree spatial resolution used by the International Land Model Benchmarking (ILAMB) modeling environment. The core domain pixels have a value of zero, while the extended domain pixels have a value of one. Pixels outside of the ABoVE study region have a value of 255. |
Attributes and Variables in the Data Files
Table 2. Attributes in the shapefile ABoVE_Study_Domain.shp
| Variable | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Region | A text field indicating the Core and Extended Region Polygons | |
| Shape_Leng | m | The geometric length of the Core and Extended Region Polygons (in meters) |
| Shape_Area | m | The geometric area of the Core and Extended Region Polygons (in sq meters) |
Table 3. Attributes in the files ABoVE_240m_30m_5m_grid_tiles.shp and ABoVE_240m_30m_5m_grid_tiles.kmz
| Attribute | Description | Number of tiles | Range of tiles |
|---|---|---|---|
| grid_level | Grid level name | all tiles | all tiles |
| grid_id | Name of grid tile | all tiles | all tiles |
| spatial_re | Spatial resolution of grid | all tiles | all tiles |
| ah | 240-meter grid tile number in the horizontal direction | 6 horizontal | h000 - h005 |
| av | 240-meter grid tile number in the vertical direction | 4 vertical | v000 - v003 |
| bh | 30-meter grid tile number in the horizontal direction | 36 horizontal | h000 - h035 |
| bv | 30-meter grid tile number in the vertical direction | 24 vertical | v000 - v023 |
| ch | 5-meter grid tile number in the horizontal direction | 216 horizontal | h000 - h215 |
| cv | 5-meter grid tile number in the vertical direction | 144 vertical | v000 - v143 |
Table 4. Variables in the raster file ABoVE_Study_Domain.tif
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Value | A unique value representing the core (Value = 1) and extended (value = 2) ABoVE Study Domain. |
| Count | The number of 1000 meter pixels for each unique value (study domains) |
Table 5. Variables in the file ABoVE_Study_Domain_ILAMB.nc
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| ids | ABoVE study domain pixel values (used by the International Land Model Benchmarking (ILAMB) modeling environment). Core domain pixels have a value of zero, while the extended domain pixels have a value of one. Pixels outside of the ABoVE study region have a value of 255. |
Spatial Reference Properties
The GeoTIFF files and shape files are in the ABoVE Standard Projection.
Projected Geographic Coordinate Reference: GCS_North_American_1983
Projection: Albers Equal Area Conic
The Canadian Albers Equal Area Conic projection system and parameters:
WKID (EPSG): 102001 Authority: ESRI
Projection: Albers Conic Equal Area
False_Easting: 0.0
False_Northing: 0.0
Central_Meridian: -96.0
Standard_Parallel_1: 50.0
Standard_Parallel_2: 70.0
Latitude_Of_Origin: 40.0
Linear Unit: Meter (1.0)
Geographic Coordinate System: GCS_North_American_1983
Angular Unit: Degree (0.0174532925199433)
Prime Meridian: Greenwich (0.0)
Datum: North_American_1983
Spheroid: GRS_1980
Semimajor Axis: 6378137.0
Semiminor Axis: 6356752.314140356
Inverse Flattening: 298.257222101
Spatial Data Properties: Raster file - GeoTIFF ABoVE_Study_Domain.tif
Spatial Representation Type: Raster
Pixel Depth: 8 bit
Pixel Type: byte
Number of Bands: 1
Band Information: ABoVE Study Domain
Raster Format: GeoTIFF
No Data Value: 127
Scale Factor: none
Offset: none
Number Columns: 4,022
Column Resolution: 1,000 meter
Number Rows: 3,565
Row Resolution: 1,000 meter
Extent in the items coordinate system
North: 4562535.093300
South: 997535.093300
West: -3398274.762900
East: 623725.237100
xll corner: -3398274.762900
yll corner: 997535.093300
Cell Geometry: area
Point in Pixel: center
NetCDF file - ABoVE_Study_Domain_ILAMB.nc
Datum: WGS 1984
Spatial resolution: half degree
Application and Derivation
ABoVE Study Domain
The core and extended regions within the ABoVE Study Domain provide the opportunity to carry out research needed to address key research questions and objectives for understanding how environmental change is causing changes to social-ecological systems across the Arctic and boreal region of western North America.
- The Core Region of the Study Domain captures the regional-scale variation in surface and atmospheric conditions necessary for the research addressing the second tier science questions and objectives of ABoVE. The Core Region encompasses a range of landscapes, with areas that are rapidly changing in complex ways in response to global-scale climate change and regional-scale disturbances as well, as others that are not - a combination that will allow for the studies on both vulnerability and resilience.
- The Study Domain also includes an Extended Region outside of the Core Region that is needed for study of a subset of important changes that are unique to these regions (for example, insect outbreaks and forest dieback in the southern boreal forest). The Extended Region provides additional opportunities for research where environmental conditions are considered to be antecedent to those in the Core Region, as well as to collaborate on research being sponsored by partners.
ABoVE Reference Grids
The ABoVE field campaign will provide the opportunity to expand and coordinate a set of focused, interdisciplinary research activities designed to further understand the causes and consequences of change in the social-ecological systems of the Arctic and boreal regions of western North America. The campaign is expected to result in the development of multiple geospatial datasets. To facilitate data interoperability, a standard projection and reference grid have been proposed to cover the ABoVE study domain.
Thematic data products will be generated from field measurements, flux towers, airborne remote sensors and satellite remote sensing data. The datasets will range considerably in resolution, format, geographic extent, projection and/or reference system. This variability in ABoVE datasets is likely to place a considerable burden on individual researchers as they will need to standardize the incoming datasets to support geospatial analysis, thus leading to duplicated effort across research groups utilizing these products. This duplication of effort will continue to propagate as outcomes of scientific analysis from individual research groups will require subsequent standardization to support their further inclusion in ABoVE science projects.
Implementing a standard projection and grid enables the producers of the data to align and subdivide data products in order to ease archiving and distribution of datasets (both for long-term archiving of the data and near-term use throughout the campaign’s duration), and simplifies data standardization for scientific analysis within ABoVE. This compatibility across multiple datasets facilitates interoperability of the datasets in scientific analysis, and is an important benefit of the standardized projection and reference grid.
Additionally, it is expected that many data products will be generated with medium to fine resolution (30-m spatial resolution or less) imagery and hence would be too large to distribute to users as single files covering the entire study region. Where the projection provides a mechanism to ensure that the products are geometrically compatible, the reference grid provides a standardized way to break the files up into units that are easy to download and manipulate by the researchers.
Gridded ABoVE datasets of the extent larger than 100 X 100-km2 are to be produced in this grid and projection (this is roughly a Landsat tile). It is recognized that, at very high resolution, reprojection of original data can result in substantial special shifts in orientation, location, and shape of small objects; therefore, ABoVE science team members are encouraged to submit their fine-scale datasets in the original projection in addition to the ABoVE grid format (if the extent of their dataset is greater or equal to 10,000-km2) or only in the original projection if it is smaller than that size.
Reference Grid Naming Convention
The reference grid naming convention is modeled after the MODIS grid using horizontal (h) and vertical (v) offsets from the upper left corner to describe the tile. For example in the left Figure 1-A (showing the large grid) the tile in the upper left corner is referred to as “h000v000” and the tile in the lower right corner is referred to as “h005v003”. The right Figure 1-B shows the smaller grid nested inside the larger grid. For each of the large tiles there is a series of small tiles nested inside. The large grid is referred to as “A”, the medium grid is referred to as “B”, and the small grid is referred to as “C”.
For the A grid:
ABoVE.water.2001001.Ah000v000.001.2014075120101.hdf
Where:
ABoVE – refers to the campaign
Water – refers to the product ID or type
2001001 – refers to the data reference date
Ah000v000 – refers to the upper left tile in the “A” or larger grid (Figure 1, Left)
001 – refers to the version of the product
2014075120101 – is a production date for the product
For the B grid:
ABoVE.water.2001001.Bh002v003.001.2014075120101.hdf
Where:
ABoVE – refers to the campaign
Water – refers to the product ID or type
2001001 – refers to the data reference date
Bh002v003 – refers to the purple tile in the “B” or medium grid (Figure 1, Right)
001 – refers to the version of the product
2014075120101 – is a production date for the product
For the C grid:
ABoVE.water.2001001.Ch014v020.001.2014075120101.hdf
Where:
ABoVE – refers to the campaign
Water – refers to the product ID or type
2001001 – refers to the data reference date
Ch014v020 – refers to the green tile in the “C” or fine grid (Figure 1, Right)
001 – refers to the version of the product
2014075120101 – is a production date for the product
Three Digit Identifiers
To simplify downstream processing it is recommended that all products use three digit identifiers for all grid tile identifiers (i.e. Ch014v020 instead of h14v20) to facilitate scripting in analyses later on.
Quality Assessment
Not applicable.
Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
The ABoVE Reference Grid is applicable mainly for raster-based products derived for the study domain (but does not apply to circumpolar datasets). The grid has been designed to cover the entire study domain, and extends to the eastern portions of North America (see Figure 1) to accommodate any products that are looking at continental scale processes. This grid is similar to the MODIS tiling scheme and is a nested set of grids provided at scales of 240, 30, and 5-meter spatial resolution, such that products from MODIS, Landsat, and very high spatial resolution (VHR) data would be compatible within the grid. It is easily scalable for products of 1 meter to 10 kilometers by switching from one grid resolution to another as the resolution gets coarser.
Reference grid nesting scheme and between grid conversion
The nesting scheme provides a standardized and straightforward tiling pattern where each of the larger tiles is composed from 6 x 6 (36) smaller tiles of the smaller grid system. For example, a single tile for the coarse resolution A-grid is contains 6 x 6 (36) tiles of B-grid. Similarly, each single tile of B-grid contains 6 x 6 (36) tiles of C-grid. Simple calculations can be used to translate between resolutions. For example:
To find the location of a given the C-grid tile Ch036v012 within B-grid, the horizontal (h036) and vertical (v012) components of the tile numbering should be divided by 6:
floor(36 / 6) = 6 and floor(12/6 = 2) (“floor” is a math function that truncates floating point values to integers without rounding)
Hence Ch036v012 is found in Bh006v002. The position of a C-grid tile within the A-grid can be determined in a similar way by dividing h and v components by 36:
floor(36/36) = 1 and floor(12/36) = 0
Hence Ch036v012 is in Ah001v000. Translating from the B-grid to the A-grid is the same as translating from C-grid to B-grid, simply divide h and v by 6.
Given Bh010v008:
floor(10/6) = 1 and floor(8/6) =1
Hence Bh010v008 is in Ah001v001. This simple translation method can facilitate analysis that requires using multiple products at varying spatial resolutions.
ABoVE: Study Domain and Standard Reference Grids
The approach taken with the ABoVE reference grid and projection is modeled after the MODIS standard products. Below is a list of assumptions that were used when determining the projection and grid:
- While the projection would be applicable to multiple data types, the grid would primarily be used for raster products produced over the study domain (not including circumpolar datasets).
- To provide areal calculations from the data products we need to have the data in an equal area projection.
- The products could range from fine spatial resolution (1 – 5 m) to coarse spatial resolution (250 m or more).
- 30 m will be a central spatial resolution.
- Users of raster data can easily download files that are 300 MB in size.
ABoVE Study Domain for ILAMB
The ABoVE study domain for ILAMB data file (ABoVE_Study_Domain_ILAMB.nc) was contributed by Renato Braghiere, Joshua Fisher, and their research project funded by ABoVE. See Braghiere et al. (2023) for more details.
Data Access
These data are available through the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC).
ABoVE: Study Domain and Standard Reference Grids, Version 2
Contact for Data Center Access Information:
- E-mail: uso@daac.ornl.gov
- Telephone: +1 (865) 241-3952
References
Braghiere, R. K., Fisher, J. B., Miner, K. R., Miller, C. E., Worden, J. R., Schimel, D. S., & Frankenberg, C. (2023). Tipping point in North American Arctic-Boreal carbon sink persists in new generation Earth system models despite reduced uncertainty. Environmental Research Letters. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ACB226
Dataset Revisions
| Version | Release Date | Revision Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | 2023-08-23 | Includes the addition of a NetCDF file of the Core and Extended study regions used by the International Land Model Benchmarking (ILAMB) modeling environment |
| 2.0 | 2017-11-29 | Includes the addition of the 5-m grid |
| 1.0 | 2017-01-12 | Initial release. |